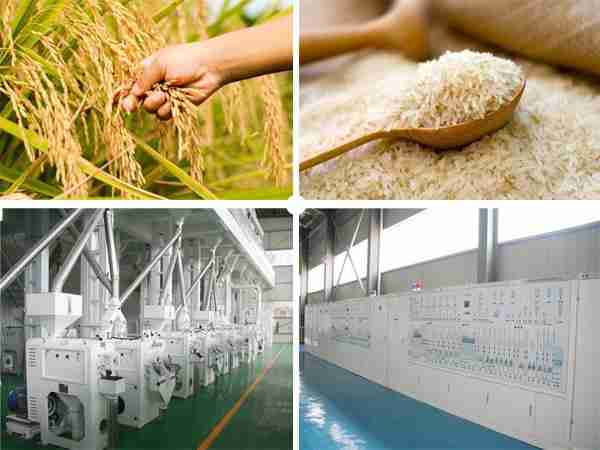
Transforming Grains: The Evolution of Rice Mill Plants
In the heart of countless cultures, rice stands as a staple food, nourishing billions and weaving its essence into the fabric of daily life. Yet, behind the simple act of cooking and consuming rice lies a complex journey of transformation, facilitated by the ingenuity of rice mill plants. From the rudimentary tools of ancient civilizations to the sophisticated machinery of today, the evolution of rice milling reflects the broader narrative of agricultural innovation and technological advancement. This article embarks on a journey through time, exploring how rice mills have adapted, advanced, and ultimately reshaped the ways in which we process and consume one of the world’s most cherished grains. Join us as we uncover the milestones in this fascinating evolution, highlighting the pivotal role that these milling plants play in ensuring food security, sustainability, and economic growth across the globe.
Understanding the Historical Journey of Rice Milling Technology
The journey of rice milling technology spans thousands of years, reflecting the ingenuity of civilizations that have relied on this staple grain. In ancient times, the process of milling was rudimentary, often achieved through manual methods such as pounding rice grains in mortars made from wood or stone. As societies advanced, so did their techniques, leading to the establishment of simple machines powered by animal labor. These early innovations laid the groundwork for a more efficient approach, ultimately leading to the creation of water-powered and wind-powered milling systems in various cultures, notably in Asia. Over time, these developments allowed for increased productivity, enabling rice to be processed on a larger scale and distributed more widely.
As the Industrial Revolution unfolded, the rice milling industry saw a significant transformation with the advent of steam-powered machines. This era brought about mechanized milling, which introduced steel rollers that could husk and whiten rice more effectively than traditional methods. The evolution didn’t stop there; the 20th century ushered in modern innovations such as electrical milling equipment and automated systems, which further revolutionized the industry. Today, rice mill plants are equipped with state-of-the-art technology that ensures a high degree of precision in processing, along with improved quality and yield. Key advancements include:
- Automated Feeding Systems – Enhancing efficiency through precise control of grain input.
- Optical Sorting Machines – Ensuring quality by removing imperfect grains.
- Integrated Quality Control – Allowing real-time monitoring of the milling process.
| Era | Key Innovations |
|---|---|
| Ancient Times | Manual pounding and grinding |
| Medieval Period | Animal-powered mills |
| Industrial Revolution | Steam-powered milling |
| Modern Era | Automated and electrical equipment |
Innovative Techniques Reshaping Modern Rice Processing
The landscape of rice processing is undergoing a remarkable transformation, driven by a series of innovative techniques that enhance efficiency and sustainability. One such technique is integrated milling, which combines multiple stages of rice processing into a single, streamlined operation. This approach reduces energy consumption and minimizes waste, resulting in a more eco-friendly process. Moreover, advancements in sensor technology allow for real-time monitoring of temperature and moisture levels, ensuring optimal processing conditions. These innovations play a crucial role in maintaining the quality of the final product while reducing the risk of spoilage.
Another significant shift is seen in the use of biotechnology, where selective breeding and genetic modifications are employed to create rice varieties that are more resistant to pests and diseases. This not only improves yield but also reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices. Furthermore, the adoption of automated systems in rice mills—such as robotic sorters and AI-driven quality control measures—enhances productivity and precision. As these technologies continue to evolve, they offer the promise of a resilient rice industry that meets the demands of a growing global population.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Integrated Milling | Reduces energy use and waste |
| Sensor Technology | Ensures optimal processing conditions |
| Biotechnology | Enhances yield and reduces pesticide use |
| Automated Systems | Improves productivity and precision |
The Role of Sustainability in Future Rice Mill Operations
The integration of sustainable practices into rice mill operations is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for future resilience and efficiency. By adopting eco-friendly technologies, mills can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and resource consumption. Key elements of sustainable rice milling include:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power can lead to substantial reductions in operating costs.
- Water Conservation: Advanced milling techniques focus on minimizing water usage, crucial in regions facing water scarcity.
- Waste Management: Utilizing by-products like rice husks and bran for bioenergy or as raw materials for other industries can promote circular economies.
Moreover, modern rice mills are increasingly recognizing the importance of certifications and compliance with environmental regulations. These include adherence to ISO standards, which not only improve operational processes but also enhance marketability. Mills pursuing sustainability may find value in tracking their progress through comprehensive reporting systems. For clarity, the table below illustrates some common sustainability certifications applicable to rice mills:
| Certification | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management system standards. | Enhances efficiency and minimizes waste. |
| Fair Trade | Focuses on equitable trading conditions. | Promotes sustainable livelihoods for farmers. |
| Rainforest Alliance | Ensures sustainability for ecosystems and communities. | Increases trust in the market for eco-friendly products. |
Maximizing Efficiency: Best Practices for Todays Rice Mill Plants
Efficiency is the heartbeat of modern rice mill plants, and embracing best practices is key to sustaining operations that are both productive and environmentally friendly. One fundamental approach is the implementation of automation systems. By integrating advanced technology throughout the milling process, plants can minimize manual labor and increase precision. This can include using automated conveyor belts, advanced husking machines, and digital monitoring systems that allow for real-time adjustments, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste. Furthermore, regular maintenance schedules for machinery can prevent unexpected downtimes, enhancing overall productivity.
Another crucial aspect is the optimization of resource management. Mills should focus on energy efficiency by adopting equipment that consumes less power and exploring renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or biomass. Additionally, waste management plays a vital role in enhancing sustainability. Practices such as utilizing rice husks as biofuel or converting by-products into animal feed not only reduce waste but also create additional revenue streams. The following table summarizes essential strategies for improving efficiency in rice milling:
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automation Technology | Increased precision, reduced manual labor |
| Regular Maintenance | Prevention of downtimes, longevity of equipment |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower operational costs, environmentally friendly |
| Waste Utilization | Reduced waste, additional revenue streams |
Wrapping Up
As we conclude our exploration of the transformative journey of rice mill plants, it becomes evident that these facilities are more than mere engines of production; they are symbols of innovation and adaptability in the agricultural landscape. From their humble beginnings to the sophisticated technology of today, rice mills have evolved to meet both the needs of farmers and the demands of a growing global population.
This evolution underscores the importance of sustainability, efficiency, and quality in food processing. Modern rice mills not only preserve the integrity of this staple grain but also contribute to the economic vitality of rural communities. As we look to the future, advancements in automation, environmental stewardship, and genetic research promise to further revolutionize this pivotal sector.
The story of rice mills is, in many ways, a reflection of our own journey toward progress. Each technological leap invites us to reflect on the delicate balance between tradition and innovation, reminding us that in the world of agriculture, the seeds of change continue to be sown. As we move forward, let us embrace these advancements while honoring the rich heritage of rice cultivation, ensuring that future generations can enjoy the fruits of this vital grain.