In the vibrant tapestry of agriculture, few threads are as intricately woven as those of rice cultivation. For millions around the globe, this staple grain is not merely a source of sustenance; it symbolizes tradition, culture, and livelihood. Yet, the journey from paddy field to plate is complex and multifaceted, reliant on a series of transformative processes that often go unnoticed. At the heart of this journey lie Paddy Processing Units—unsung heroes in the agricultural landscape. These facilities do more than simply mill rice; they enhance quality, foster economic growth, and cater to the expanding demands of a rapidly evolving market. This article delves into the essential role of paddy processing units, exploring how they not only revolutionize the harvest but also support farmers and communities worldwide, ultimately shaping the future of food security and sustainability. Join us as we unveil the intricate dance of innovation and tradition that defines paddy processing, illuminating its significance in the broader narrative of agriculture and society.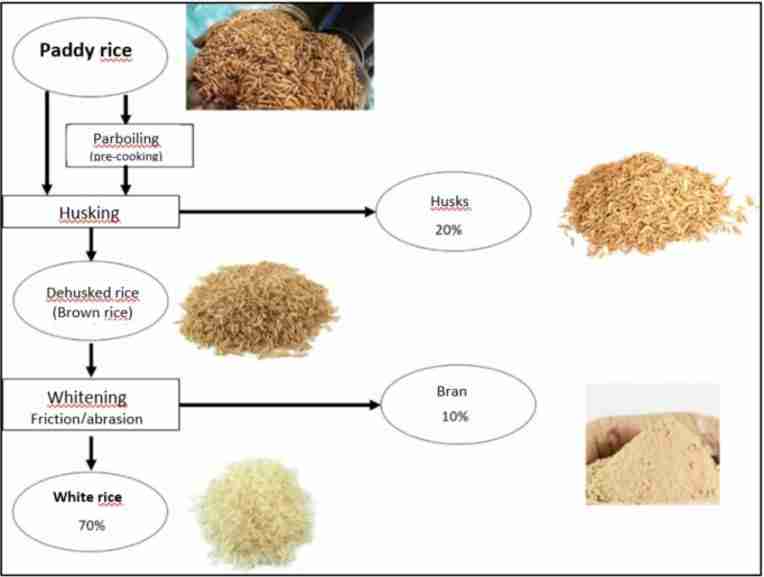
Understanding the Paddy Processing Journey from Field to Table
Paddy processing is an intricate journey that transforms raw grains into the versatile staple we rely on daily. From the moment the rice is harvested, the unhusked rice—known as paddy—embarks on a detailed process designed to enhance its quality and market value. The initial phase involves drying, where harvested paddy is spread under the sun or in specialized machines to reduce moisture content. This step is crucial in preventing spoilage and ensuring long-term storage viability. Once adequately dried, the paddy undergoes cleaning to remove impurities, which may include dust, stones, and unwanted grains, ensuring only the best quality rice proceeds to the next stage.
As the processing journey advances, the paddy enters the milling phase, where husks are separated from the grains. This can be achieved through different types of mills, each selected based on desired quality attributes. The resulting brown rice—rice with the bran layer intact—can be polished to produce white rice, a ubiquitous component of numerous cuisines worldwide. the processed rice must be packaged efficiently for distribution. Proper packaging not only preserves freshness but also enhances consumer appeal. The journey from field to table is complete when this packaged rice reaches supermarkets, local markets, or directly to our kitchens, ready to enrich our daily meals.
| Processing Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Drying | Reduces moisture content to prevent spoilage. |
| Cleaning | Removes impurities like dirt and unwanted grains. |
| Milling | Separates husks from grains to produce brown or white rice. |
| Packaging | Preserves freshness and appeals to consumers. |

Enhancing Quality and Efficiency through Technological Innovation
Paddy processing units have emerged as beacons of advancement, integrating state-of-the-art technology to streamline operations and maximize outputs. By adopting automated milling systems, these facilities enhance both the quality of rice produced and overall efficiency. No longer dependent on traditional methods, producers can leverage advanced machinery that ensures precise milling, reducing waste and optimizing the yield. This transformation results in a product that meets global standards, elevating the competitive edge of local farmers while boosting consumer satisfaction.
Furthermore, the integration of data analytics within paddy processing allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on real-time information. Through technologies such as IoT and machine learning, processors can monitor quality control, track supply chain metrics, and predict market trends. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters sustainable practices by minimizing resource consumption. A structured approach to technological integration benefits all involved in the ecosystem—from farmers to consumers—creating a symbiotic relationship that promotes growth and sustainability.
| Technological Innovations | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Automated Milling Systems | Increased efficiency, reduced waste |
| Data Analytics | Informed decision-making, market insight |
| IoT Integration | Real-time monitoring, enhanced quality control |
| Machine Learning | Predictive analysis, optimized operations |
Sustainable Practices in Paddy Processing for Environmental Balance
In the quest for environmental stewardship, paddy processing units are increasingly adopting sustainable practices that not only enhance productivity but also promote ecological harmony. By integrating methods that reduce waste and conserve resources, these units are transforming the landscape of agricultural processing. Some noteworthy sustainable practices include:
- Water Conservation: Employing techniques such as recirculating water systems and rainwater harvesting to minimize water usage.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing renewable energy sources, like solar panels and biogas systems, to power machinery and reduce carbon footprints.
- Waste Management: Composting organic waste and repurposing by-products for animal feed or biofertilizers.
Moreover, the shift towards eco-friendly practices in paddy processing not only contributes to environmental balance but also yields economic benefits. By implementing sustainable measures, processing units can lower operational costs and enhance product quality. A comparison of traditional versus sustainable practices can highlight these advantages effectively:
| Aspect | Traditional Practices | Sustainable Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage | High | Reduced |
| Energy Source | Fossil Fuels | Renewable Energy |
| Waste Output | Significant | Minimized |
This comparative analysis showcases the potential of paddy processing units to play a vital role in environmental preservation while simultaneously improving their operational efficiency. By committing to sustainable practices, these units not only support agricultural sustainability but also ensure a more resilient ecological future.
Empowering Local Economies: The Impact of Processing Units on Rural Livelihoods
The establishment of paddy processing units in rural areas serves as a catalyst for economic development, providing numerous benefits that ripple through local communities. These facilities play a crucial role in enhancing income opportunities for farmers, allowing them to maximize the value of their harvests. By processing their paddy on-site, farmers can transform raw grain into market-ready products, thus increasing their profit margins. The following key aspects illustrate how processing units empower local economies:
- Job Creation: Processing units employ local workers, thus reducing unemployment rates and boosting household incomes.
- Increased Market Access: Processed rice is more appealing to buyers, improving sales and generating a steady stream of revenue for farmers.
- Skill Development: Training programs associated with processing units enhance the skill sets of local workers, promoting long-term economic resilience.
- Value Addition: By adding value to paddy through processing, the overall economic worth of the crop increases, benefiting the entire community.
In addition to immediate economic benefits, processing units contribute to the sustainability of rural livelihoods by fostering a sense of community and collaboration among farmers. Collective efforts among smallholder farmers lead to shared resources and knowledge, enhancing productivity and innovation. By investing in infrastructure such as storage facilities and modern machinery, rural areas can effectively manage supply chains and reduce post-harvest losses. The following table summarizes some of the key benefits of processing units on rural livelihoods:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Economic Diversification | Encourages farmers to engage in multiple income-generating activities. |
| Community Development | Strengthens local networks and collaboration for common goals. |
| Sustainable Practices | Promotes environmentally friendly farming and processing techniques. |
Future Outlook
the journey of rice from field to table is a complex tapestry woven with the threads of tradition, innovation, and sustainability. Paddy processing units stand as the unsung heroes in this narrative, enhancing the quality of the grain, optimizing yields, and ensuring that every harvest is transformed into a source of nourishment for millions. As we look toward the future, it is imperative to recognize and support these vital units, not only for their role in preserving agricultural heritage but also for their potential to meet the challenges of modern food production. By fostering advancements in processing technologies and championing sustainable practices, we can ensure that the fruits of our labor are cultivated with care and delivered with purpose. Ultimately, the transformation of harvests into wholesome rice reflects our commitment to feeding both present and future generations, making the role of paddy processing units more essential than ever.






