Unveiling the Secrets of Rice Processing: From Field to Table
Rice, a humble grain that nourishes over half of the world’s population, carries within it a journey as intricate as the cultures that cherish it. From the sun-drenched paddy fields where it sways gently in the breeze, to the steaming bowls that grace our dinner tables, the path of rice is paved with age-old traditions and modern innovations alike. But how does the ordinary grain transform into the staple food that unites families and fuels communities? In this exploration of rice processing, we peel back the layers of this fascinating journey, revealing the careful cultivation, meticulous harvesting, and intricate processing techniques that ensure each grain meets the highest standards of quality. Join us as we delve into the secrets behind one of humanity’s oldest crops, uncovering the art and science that bring rice from its natural habitat to the plates of millions around the globe.
Understanding Rice Cultivation Techniques for Optimal Yield
Rice cultivation is both an art and a science, requiring a blend of traditional practices and modern techniques to achieve the best possible yield. Soil preparation is the crucial first step, where farmers meticulously till and aerate the land to encourage healthy root growth. The choice of seed variety also plays a significant role, as it determines not only the yield but also the resistance to pests and diseases. Furthermore, the incorporation of crop rotation practices can significantly enhance soil fertility, allowing the following rice crops to thrive. Proper water management is vital, as rice is generally grown in flooded conditions; thus, understanding the local irrigation systems is essential to ensure optimum growth conditions throughout the crop’s lifecycle.
Another key factor in achieving high yield is diligent pest and weed control. Farmers employ integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including biological, cultural, and mechanical methods, to minimize crop loss without relying solely on chemical applications. Additionally, timely fertilization is critical to provide essential nutrients that foster growth, with many choosing organic options to improve soil health long-term. Data-driven approaches, such as precision farming, have also gained traction, allowing cultivators to analyze the land’s requirements accurately and adjust their practices as needed. By understanding and implementing these varied techniques, rice farmers can significantly enhance productivity, ultimately ensuring that this staple food continues to nourish millions around the globe.
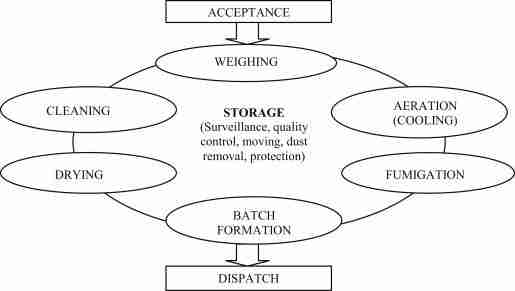
Exploring Post-Harvest Processing Methods for Quality Preservation
In the journey from golden fields to hearty tables, post-harvest processing plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the quality of rice. One of the first challenges after harvest is to prevent moisture damage, which can lead to spoilage. Drying is an essential step that involves reducing the moisture content of rice grains to an optimal level, typically around 14%. Various methods, including sun drying and mechanical drying, are employed to achieve this target. Additionally, milling is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and marketability of the rice. This process removes the husk and bran layers, transforming rough paddy grains into shiny white rice while also affecting its nutritional value. To further preserve the quality, techniques such as cool storage and packaging in airtight containers are implemented to minimize exposure to pests and environmental factors.
Another innovative approach in post-harvest processing is fortification, where nutrients are added to the rice to enhance its health benefits. This method can significantly improve the nutritional profile, especially in regions where rice is a staple food. Furthermore, parboiling has gained popularity as a technique that not only improves the shelf life of rice but also enhances its nutritional value. This technique involves soaking the rice grains and then partially boiling them before drying and milling. The table below summarizes these processing methods and their benefits:
| Processing Method | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drying | Reduces spoilage and moisture content |
| Milling | Removes husk; improves appearance |
| Cool Storage | Prevents pest infestation |
| Fortification | Enhances nutritional content |
| Parboiling | Improves shelf life and nutrition |
The Journey of Rice Milling: Transforming Grain into Culinary Staple
The journey of transforming rice from its raw form into a beloved culinary staple involves a meticulous process that balances tradition with modern technology. The initial stage begins in the vast paddy fields where farmers diligently cultivate rice varieties that thrive in diverse climates. Once harvested, the rice grains enter the milling phase, where they undergo several crucial transformations. During milling, the outer husk is removed to reveal the brown rice beneath, which then undergoes further polishing to produce white rice, often chosen for its aesthetic appeal and softer texture. This intricate process not only enhances the shelf life and culinary qualities but also reflects a deep connection between cultures and cuisine.
Highly specialized machinery plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the rice maintains its nutritional value while achieving optimal quality. Various steps involve:
- Husking: The outer shell is eliminated, marking the first step towards milling.
- Brown Rice Production: The remaining grain has the bran intact, containing essential nutrients.
- Whitening: This step polishes the rice, yielding the familiar white grain.
- Grading: The final products are sorted based on size, shape, and quality.
Additionally, quality assurance is integral to this process, with checks in place to maintain high standards. The final outcome is presented in various forms, catering to diverse culinary practices worldwide. Here’s a simplified representation of the rice processing stages:
| Processing Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collecting ripe rice from the fields. |
| Husking | Removing the rough outer layer. |
| Milling | Refining brown rice into white rice. |
| Grading | Sorting based on quality and size. |
This exciting journey not only results in a staple food enjoyed across the globe but also highlights the synergy between nature and human ingenuity, manifesting in every delicious bite of rice.
Sustainable Practices in Rice Processing for a Greener Future
In the quest for a more environmentally friendly approach to agriculture, innovative technologies and traditional knowledge are merging to create sustainable practices in rice processing. This new wave of strategies not only focuses on reducing the carbon footprint but also emphasizes resource efficiency and waste reduction throughout the production cycle. For instance, utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar panels in milling operations can drastically cut down on the emissions associated with fossil fuel consumption. Additionally, the implementation of water-efficient irrigation techniques and organic farming methods can significantly diminish the environmental impact of rice cultivation.
Furthermore, the adoption of circular economy principles is making strides in rice processing facilities. This approach includes repurposing by-products such as rice husks and straw into valuable resources, which can be transformed into biofuel or biodegradable packaging. Furthermore, improved water management practices are essential to minimize wastage and promote aquifer recharge. The following table provides a glimpse into these sustainable initiatives:
| Sustainable Initiative | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Usage | Reduces carbon emissions |
| Water-Efficient Irrigation | Conserves water resources |
| By-Product Recycling | Reduces waste and generates income |
| Organic Farming Methods | Promotes soil health and biodiversity |
Key Takeaways
the journey of rice from field to table is a remarkable tale of transformation, intricately weaving together the efforts of farmers, processors, and chefs alike. Each step in the rice processing journey—be it harvesting, milling, or packaging—carries with it a history of tradition and innovation. By peeling back the layers of this staple grain’s lifecycle, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the food on our plates but also the people and practices that sustain it.
As we savor a warm bowl of rice, let us remember the dedication that goes into every grain, the environmental resilience required to cultivate it, and the intricate processes that refine its flavors and textures. The next time you partake in this global staple, consider the hidden stories and secrets encapsulated within. In embracing this knowledge, we not only celebrate the humble rice but also foster a connection to the broader agricultural narrative that sustains our world. So, the next time you sit down for a meal, take a moment to reflect on the journey of rice—filling not just our plates, but our understanding of the intricate dance between nature and nourishment.