Unveiling the Journey: Inside a Parboiled Rice Processing Plant
In the heart of agricultural landscapes, where sprawling fields sway gently under the sun, lies a hidden realm of transformation—an ordinary grain’s metamorphosis into a staple for millions. Parboiled rice, renowned for its distinct texture and enhanced nutritional profile, undergoes a meticulous journey from harvest to plate, one that often goes unnoticed by the average consumer. This article invites readers to embark on an enlightening exploration inside a parboiled rice processing plant, where technology and tradition coalesce in a symphony of machinery and human expertise. As we peel back the layers of this fascinating process, we will uncover the science, craftsmanship, and cultural significance that elevate this humble grain to its rightful place in kitchens around the world. Join us as we unravel the intricate steps that define the life cycle of parboiled rice, highlighting the dedication and innovation that fuel this essential industry.
Understanding the Parboiling Process from Paddy to Perfection
The journey from raw paddy to perfectly parboiled rice is a fascinating one, encompassing several intricate processes that transform the grain while enhancing its nutritional value and flavor. Parboiling, a technique that involves partially boiling the raw rice before milling, serves multiple purposes. This process not only gelatinizes the starch, making the rice more digestible, but also helps in retaining vital nutrients that might be lost during traditional milling. Typically, the parboiling process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Soaking: Raw paddy is soaked in warm water to prepare it for partial boiling.
- Steaming: The soaked paddy is then steamed, allowing for the conversion of starches.
- Drying: Once steamed, the paddy is dried to reduce moisture content before milling.
- Milling: the dried paddy is milled to remove the husk and bran layers, yielding the finished parboiled rice.
This meticulous process not only enhances the grain’s taste and texture but also contributes to its shelf life and cooking quality. An efficient parboiled rice processing plant ensures that these stages are executed under carefully controlled conditions to maintain quality. Below is a simplified table that outlines the physical changes rice undergoes during the parboiling process:
| Stage | Physical Change |
|---|---|
| Soaking | Increased moisture content |
| Steaming | Starch gelatinization |
| Drying | Reduced moisture for storage |
| Milling | Removal of husk and bran |

Exploring the Role of Technology in Enhancing Efficiency
In the heart of a parboiled rice processing plant, technology serves as the backbone of operations, infusing every stage of production with precision and speed. Automation and smart machinery have transformed traditional methods, allowing for a seamless flow from paddy to packaged product. Key technological advancements include:
- Automated Sorting Systems: Utilizing advanced sensors and imaging technology, these systems ensure that only high-quality grains make it through, drastically reducing human error.
- Temperature Control Mechanisms: Maintaining optimal conditions during parboiling is essential; sophisticated controls monitor and adjust temperature, ensuring uniform cooking and nutrient retention.
- Data Analytics Software: This allows plant managers to track production metrics in real-time, leading to informed decisions that bolster efficiency and reduce downtime.
Moreover, with the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, connectivity between machines has resulted in a fine-tuned operation where data flows seamlessly. This interconnectedness enables preventive maintenance, minimizing interruptions in production. Below is a concise comparison of traditional versus modern techniques in rice processing:
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | Modern Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Lower outputs, time-consuming | Higher outputs, quicker processes |
| Quality Control | Manual checking, higher risk of defects | Automated sorting, fewer defects |
| Energy Use | Higher consumption due to inefficiency | Optimized energy use through precision |
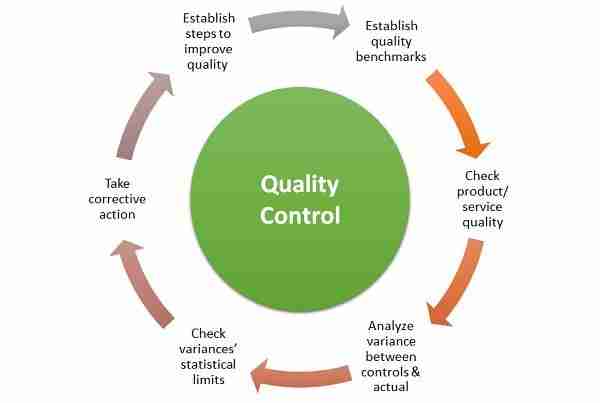
Quality Control Measures: Ensuring Consistency in Every Grain
In parboiled rice processing, quality control measures are pivotal in maintaining the integrity of each grain. From the moment paddy enters the plant, various stages are carefully monitored to ensure that the end product meets high standards. Operators conduct routine inspections and employ advanced technology to detect any variations or defects early in the process. This proactive approach helps in minimizing waste and guaranteeing that only the best grains progress along the production line. Key measures include:
- Visual inspections at receiving stations to assess quality and grade.
- Moisture content analysis to prevent spoilage during storage.
- Color sorting machines that eliminate discolored grains.
- Chemical testing to ensure adherence to food safety regulations.
The meticulous nature of these quality control practices culminates in a series of tests that determine the physical characteristics of the rice. A comprehensive tracking system is also utilized to trace back any issues to their source, ensuring accountability and continual improvement in production standards. Below is a table summarizing the most common quality parameters assessed:
| Quality Parameter | Standard Measurement |
|---|---|
| Moisture Content | 12-14% |
| Grain Length | 6-7 mm |
| Purity Level | Minimum 97% |
| Foreign Matter | Less than 0.5% |
Ultimately, the integration of technology and rigorous testing processes ensures that every grain of parboiled rice leaving the plant is consistent in quality, thus meeting consumer expectations and culinary requirements. This ongoing commitment to excellence creates a foundation for building trust with customers, reinforcing the brand’s reputation in the competitive market.
Sustainable Practices in Rice Processing: A Path Towards Eco-Friendliness
In the realm of rice processing, sustainability isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental approach woven into the operational fabric of modern parboiling plants. Utilizing innovative techniques, these facilities are reimagining traditional practices to significantly reduce their environmental footprint. Key methods include:
- Water Conservation: Implementing closed-loop water systems that recycle water for multiple uses, effectively cutting down waste.
- Solar Energy Integration: Harnessing solar power for energy needs, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Utilization: Transforming byproducts into valuable resources, such as using husk for biofuel or promoting composting practices.
Additionally, many processing units are adopting certified organic practices and sustainable sourcing methods that foster biodiversity and promote healthier ecosystems. For instance, partnerships with local farmers that focus on organic rice cultivation not only encourage sustainable farming but also enhance community resilience. This commitment to eco-friendliness extends to the logistics of rice distribution, where optimized transport routes are employed to lower carbon emissions:
| Logistics Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Direct Farmer Partnerships | Reduces transport times and emissions |
| Eco-Friendly Packaging | Minimizes waste and promotes recycling |
| Route Optimization Tools | Cuts fuel consumption by 20% |
The Way Forward
As we draw the curtains on our exploration through the intricate world of parboiled rice processing, we hope to have shed light on the remarkable journey this humble grain undertakes, from paddy to plate. The processes that unfold within the walls of a processing plant are a testament to human ingenuity and the profound connection we share with our food. Each step, from soaking and steaming to drying and milling, not only preserves the rice’s nutritional integrity but also enhances its flavor and texture, making it a staple in kitchens worldwide.
By unveiling the intricacies of parboiling, we appreciate the skill and precision required to transform raw grain into a versatile and cherished staple. This journey not only signifies the efficiencies and innovations within the food production landscape but also emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices in the face of increasing global demands.
As you reflect on the journey of parboiled rice from the fields to your dining table, consider the stories that each grain carries—stories of tradition, labor, and culinary culture. the next time you savor a bowl of parboiled rice, remember that you are partaking in a process that transcends time and geography, bringing people together with every bite. Thank you for joining us in this fascinating exploration, and may your future culinary adventures inspire even deeper appreciation for the journey of food.