Unlocking Nutrition: Inside a Parboiled Rice Processing Plant
Rice is more than just a staple food; it’s a cultural cornerstone, a symbol of sustenance, and a vital part of diets across the globe. Yet, behind the simple grain we often take for granted lies a fascinating and intricate process that transforms raw, unrefined rice into a beloved dish on our tables. Welcome to the world of parboiled rice—a unique method that enhances the nutritional value of rice while ensuring superior taste and texture. In this article, we journey into the heart of a parboiled rice processing plant, where science meets tradition, and every step of the production process is carefully crafted to unlock the grain’s potential. Join us as we explore the technology, artistry, and dedication that go into creating this nutritious staple, revealing how it not only nourishes but also connects communities and cultivates a future where food security is within reach.
Exploring the Parboiling Process and Its Nutritional Benefits
Parboiling, an intriguing technique used in rice processing, begins with soaking the grains in water before steaming them under pressure. This process not only alters the texture and flavor of the rice, making it more palatable, but it also enhances its nutritional profile. The heat and moisture facilitate the migration of nutrients from the bran into the endosperm, thus retaining valuable vitamins and minerals that are often lost in white rice. Here are some of the key nutritional benefits associated with parboiling:
- Increased Nutrient Retention: More B vitamins and minerals are preserved compared to regular white rice.
- Lower Glycemic Index: Parboiled rice has a lower glycemic index, making it a better option for blood sugar management.
- Improved Digestibility: The process makes the rice easier to digest, making it suitable for a wider range of diets.
- Enhanced Cooking Properties: The grains remain firm and separate after cooking, reducing the chance of them becoming mushy.
In terms of the practical benefits for consumers, parboiled rice not only preserves more nutrients but also holds its structure better during cooking. This is largely due to the gelatinization of starches that occurs during the parboiling process. When examining various types of rice, the comparison is clear:
| Type of Rice | Nutritional Value (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| White Rice | 130 kcal, 2g protein, 28g carbs, 0.3g fiber |
| Brown Rice | 111 kcal, 2.6g protein, 24g carbs, 1.8g fiber |
| Parboiled Rice | 123 kcal, 2.5g protein, 26g carbs, 0.5g fiber |
Behind the Scenes: Technology and Techniques in Rice Processing
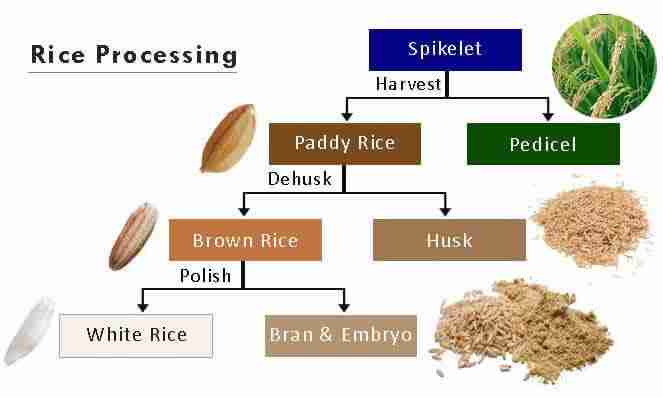
In the heart of a parboiled rice processing plant, a meticulous symphony of technology and technique unfolds. Each grain of rice undergoes a transformation that not only enhances its nutritional profile but also improves its cooking properties. The process begins with soaking, where rice grains are submerged in warm water. This step, essential for initiating the gelatinization of starches, plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product retains optimal moisture content and flavor. Following soaking, the grains are subjected to steaming, which further develops their nutritional integrity by activating vitamins, minerals, and beneficial phytochemicals.
As the processing continues, advanced machinery takes center stage. Drying units carefully control temperature and airflow, ensuring that the rice is neither over-dried nor under-dried, thus maintaining quality. This is followed by milling, where the outer husk and bran layers are removed. The final stages involve rigorous quality control measures where samples are tested for consistency, moisture levels, and taste. Each step is handled with precision, as the combinatory use of water, heat, and cutting-edge technology permits a remarkable transformation from raw grain to ready-to-cook parboiled rice. Below is a simplified overview of the processes involved:
| Process Stage | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Soaking | Submerging grains in warm water | Begins starch gelatinization and moisture absorption |
| Steaming | Heating grains with steam | Activates nutritional components |
| Drying | Controlling temperature and airflow | Preserves optimal moisture content |
| Milling | Removing husk and bran layers | Enhances texture and digestibility |
Quality Control Measures That Ensure Nutritional Integrity
At the heart of a parboiled rice processing plant lies a meticulous system of quality control measures designed to preserve the nutritional integrity of the grain. Each step in the production process is carefully monitored to ensure that essential nutrients remain intact. To facilitate this, plants implement a range of practices, including:
- Strict Sourcing Guidelines: Only high-grade paddy rice is selected from trusted suppliers to minimize contamination.
- Controlled Parboiling Processes: Precise temperature and pressure controls during parboiling activate nutrients while preventing degradation.
- Regular Laboratory Testing: Samples are tested for moisture content, vitamin retention, and possible contaminants at various stages.
Furthermore, rigorous inspection protocols enforce standards that maintain the quality of the final product. From the moment the paddy enters the facility to when the finished rice is packaged, these measures are pivotal in safeguarding both flavor and nutritional content. Key aspects of post-processing quality checks include:
| Quality Check | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Level Assessment | Every Batch | Maintaining ideal moisture for preservation |
| Nutritional Content Analysis | Weekly | Ensure nutrient retention |
| Contaminant Testing | Monthly | Check for toxins and foreign materials |
Sustainable Practices in Parboiled Rice Production and Consumption
Incorporating sustainable practices into the production and consumption of parboiled rice is essential for minimizing environmental impacts and promoting health. One major approach involves water conservation during the processing stages. By implementing techniques such as rainwater harvesting and employing efficient irrigation systems, the industry can significantly reduce water usage. Additional strategies include utilizing renewable energy sources like solar or biogas to power processing plants, which decreases reliance on fossil fuels. The adoption of sustainable pest management and soil enhancement practices can also help maintain ecosystem balance, ensuring that the quality of both soil and crop is preserved.
On the consumer side, encouraging responsible consumption can lead to more sustainable rice production. Consumers can adopt practices such as buying local or organic parboiled rice, which often involve fewer carbon emissions during transportation. Educating individuals on the nutritional benefits of parboiled rice can also play a role in supporting sustainable practices. For example, by promoting its high fiber and nutrient content, the market can witness enhanced demand for parboiled rice, thus encouraging farmers to adopt more sustainable cultivation techniques. Furthermore, consumers are encouraged to embrace meal planning and portion control to minimize waste, ensuring that every grain contributes to a more sustainable food system.
| Benefits of Sustainable Parboiled Rice Practices | Details |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Reduces water usage and promotes biodiversity. |
| Energy Efficiency | Utilizes renewable energy sources to decrease carbon footprint. |
| Health Benefits | Enhances nutritional quality, boosting community health. |
| Community Support | Encourages local economies and sustainable farming practices. |
The Way Forward
As we conclude our exploration of the intricate world of parboiled rice processing, we uncover not just the mechanics of production, but a celebration of nutritional potential. The journey of each grain, from paddy to pantry, illuminates the delicate balance between technology and tradition, efficiency and health. In these bustling processing plants, the age-old grain is transformed, fortified with nutrients that promise to nourish communities far beyond their fields.
Understanding the process of parboiling opens the door to appreciating the value of rice as an essential dietary staple. It serves as a testament to human ingenuity and a reminder of our connection to the land. As we move forward in our culinary adventures, let us not forget the stories behind our food—stories woven through time, culture, and innovative practices that continue to evolve.
the next time you savor a plate of fluffy parboiled rice, remember that it is more than just a side dish; it’s a culmination of science, care, and history. Join us in celebrating the nutritional legacy embedded in each grain, as we continue to unlock the endless possibilities of food processing for healthier futures.