In an age where culinary traditions intertwine with technological advancements, the humble grain of rice finds itself at the center of a fascinating evolution. Once harvested by hand and milled in small village setups, rice processing has undergone a stunning transformation into a high-tech industry that caters to the demands of a global market. As we delve into the journey of modern rice mills today, we will explore how innovation meets tradition, revealing the intricate dance between machinery and nature. From the fields to the processing floor, this article will illuminate the challenges and triumphs that define the contemporary landscape of rice milling, showcasing how these mills not only sustain communities but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Join us as we navigate the paths forged by modern rice mills, where every grain tells a story of resilience, adaptation, and progress.
Exploring Technological Innovations in Modern Rice Milling
Modern rice milling has undergone a dramatic transformation, embracing innovative technologies that revolutionize traditional practices. At the core of these advancements is the integration of automation and AI-driven processes, which enhance efficiency and consistency. Automation not only speeds up production but also minimizes labor costs, allowing for more scalability. Milling operations leverage sophisticated machinery capable of precise sorting, cleaning, and grinding of rice grains, ensuring optimal quality. For instance, optical sorters equipped with advanced imaging technology can detect even the slightest discrepancies in grain quality, ensuring only the best rice reaches consumers’ tables.
Moreover, the adoption of sustainable practices is becoming increasingly prevalent within modern rice mills. To reduce their environmental impact, many mills are employing energy-efficient machinery and exploring the utilization of renewable energy sources. Notably, the waste by-products from milling processes—such as husks and bran—are now being repurposed into valuable resources. This not only contributes to a circular economy model, where waste is minimized, but also offers additional revenue streams. The table below highlights some of these remarkable technological innovations and their benefits:
| Innovation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| AI Sorting Systems | Enhanced grain quality assessment |
| Energy-efficient Mills | Reduced operational costs |
| Waste Repurposing Techniques | New revenue opportunities |
| Automated Process Controls | Increased throughput and consistency |
This fusion of technology and sustainability not only reflects the needs of contemporary society but also sets the stage for the future of agriculture. Through these innovations, modern rice milling is positioned to tackle challenges such as resource scarcity and quality assurance while continuing to meet the ever-growing global demand for rice.
Sustainable Practices Transforming the Rice Industry
The rice industry is experiencing a significant transformation as it embraces sustainable practices that not only benefit the environment but also enhance the quality and efficiency of production. Modern rice mills are adopting innovative methods that reduce their carbon footprint while improving crop yields. Some notable practices include:
- Water Management: Implementing advanced irrigation techniques, such as drip or sprinkler systems, ensures optimal water usage and reduces waste.
- Organic Farming: Shifting towards organic cultivation methods minimizes the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting healthier soil and biodiversity.
- Waste Utilization: Strategies for repurposing by-products, such as rice husks, into biomass energy or building materials, exemplify a circular economy approach.
These forward-thinking approaches are quantifiable in terms of their impact. For instance, a recent study showcased how these sustainable practices yield not just environmental benefits, but also financial ones:
| Practice | Environmental Impact | Economic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Reduced water usage by 30% | Lowered operational costs by 25% |
| Organic Cultivation | Enhanced soil health | Higher market prices for organic rice |
| Biomass Energy | Minimized waste output | Added revenue from energy sales |
Through continuous innovation and commitment to sustainability, the rice industry is not only preserving its heritage but also paving the way for future generations to enjoy the delicacy of rice in an environmentally sound manner. These efforts are fostering a new narrative around rice production, turning traditional concerns into opportunities for growth and resilience in a changing world.
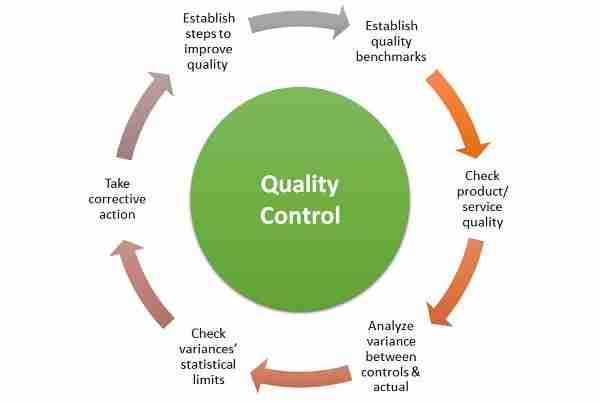
Quality Control Strategies for Superior Rice Production
Quality control in rice production has evolved into a multifaceted strategy that ensures every grain meets the highest standards of quality. Modern mills employ a range of sophisticated techniques aimed at enhancing both the safety and flavor of rice. These methods include visual inspections, where trained personnel evaluate the rice for defects, and advanced grading technologies that use machine learning algorithms to assess rice quality based on its size, color, and texture. Additional practices like moisture content testing play a crucial role in preventing spoilage and maintaining freshness.
To further bolster the integrity of the product, many mills are implementing comprehensive traceability systems. This allows producers to monitor rice from the field to the final packaging, thereby guaranteeing transparency and accountability. Information such as origin, harvesting methods, and processing details can be easily accessed, providing consumers with a reassuring sense of trust in their rice purchases. A robust quality control program also includes regular training for personnel on sanitation procedures and updates on the latest industry standards, ensuring that every step of production aligns with contemporary best practices.
| Quality Control Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspections | Trained staff check for physical defects in rice. |
| Grading Technologies | Machine learning algorithms assess size, color, texture. |
| Moisture Testing | Prevents spoilage, maintains freshness. |
| Traceability Systems | Monitors rice from field to packaging for transparency. |
The Future of Rice Mills: Trends and Opportunities Ahead
The landscape of rice milling is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As mills evolve, they’re increasingly adopting smart technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices and AI-driven analytics. These innovations not only enhance operational efficiency but also improve the quality of the final product. For instance, real-time monitoring systems can detect issues during production, allowing for immediate adjustments and minimizing waste. In addition, the pressure for sustainable practices is propelling mills towards eco-friendly techniques, which prioritize energy efficiency and water conservation, enabling them to align with global sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the demand for specialty rice varieties presents a lucrative opportunity for mills looking to differentiate themselves in the market. By diversifying their product lines to include organic, aromatic, or fortified rice, mills can cater to rising health-conscious consumer trends. Additionally, establishing partnerships with local farmers can enhance traceability and community support, leveraging the growing popularity of farm-to-table practices. As the mill industry embraces these trends, the future looks bright for those willing to innovate and adapt:
- Integration of renewable energy sources to reduce operational costs.
- Enhanced digital marketing strategies to reach new consumer segments.
- Implementation of smart inventory systems for better supply chain management.
In Retrospect
As we draw the curtains on our exploration of modern rice mills, it’s clear that the journey of grains transcends mere processing; it embodies the pulse of innovation, tradition, and sustainability. From the ingenious machinery that replaces the labor of yesteryears to the meticulous processes ensuring quality and safety, rice mills today are at the forefront of agricultural advancement. Embracing both age-old methods and cutting-edge technology, these mills not only transform paddy into edible grains but also shape the socio-economic landscape of their communities.
As we look ahead, the future of rice milling seems poised for exciting developments, guided by the dual forces of environmental stewardship and consumer demand for transparency. The journey of grains continues, reminding us that every bowl of rice carries with it a story — a narrative woven from the fields of farmers, the gears of modern mills, and the ever-evolving tastes of consumers. In the dance of tradition and innovation, the humble grain finds its place at the table, nourishing not just the body, but the connections we share.