Title: Exploring the Inner Workings of a Rice Mill Plant: A Journey Through Grain Transformation
In an era where the journey from farm to table is a topic of increasing interest, few processes are as intricate and fascinating as the milling of rice. These little grains, foundational to countless cuisines and cultures, undergo a remarkable transformation that begins with the careful harvesting of paddy and culminates in the gleaming white or brown rice that fills our pantries. But what happens behind the scenes in a rice mill plant? This article invites you to step inside these bustling facilities, where technology and tradition converge to refine raw grain into a staple food. From the rhythmic hum of machinery to the delicate balancing of nature’s bounty, join us as we explore the inner workings of a rice mill plant, uncovering the meticulous processes that ensure quality and efficiency in every grain.
Understanding the Machinery: Key Components of Rice Milling Operations
Rice milling is a complex process that involves several key components working in harmony to transform paddy rice into polished and market-ready grains. The primary machinery consists of the huller, which removes the outer husk, and the whitener, which polishes the rice to enhance its appeal. Each of these components plays a vital role in determining the quality of the final product. Other important machines include the separator, which divides the unhulled rice from the finished product, and the sifter, tasked with ensuring uniformity by removing any broken or irregular grains. Efficient functioning of these machines significantly impacts throughput and overall yield.
To understand the intricate interplay of these systems, it’s essential to consider their specific functions and the tech that powers them. Many rice mills are equipped with advanced automation systems that allow for precise control over each stage of milling, thus improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. Additionally, the de-stoner removes impurities like stones and dirt, ensuring that the rice is clean before packaging. The following table provides a concise overview of the primary components and their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Huller | Removes the husk from the paddy rice. |
| Whitener | Polishes the rice to achieve a shiny finish. |
| Separator | Separates broken rice from whole grains. |
| Sifter | Ensures uniformity by filtering out irregular grains. |
| De-stoner | Removes stones and other impurities. |
Optimizing Efficiency: Best Practices in Rice Processing Techniques
In a thriving rice mill plant, optimizing operational efficiency is paramount to maximizing output and reducing waste. Achieving streamlined processes involves integrating advanced machinery and employing meticulous techniques throughout the production line. Choices made during the selection of rice grains, milling techniques, and post-processing activities significantly impact the overall quality and yield of the final product. By focusing on the following best practices, rice mills can ensure a smoother workflow and enhanced productivity:
- Implementing automated systems: Automation reduces human error, increases consistency, and speeds up operations.
- Regular maintenance of machinery: A well-maintained machine operates more efficiently and reduces downtime.
- Train staff: Offering ongoing training ensures that employees are skilled in both the operations and safety procedures.
- Quality control: Establishing quality checkpoints throughout the milling process helps maintain high standards.
Additionally, the use of appropriate processing techniques plays a crucial role in enhancing yield and quality. For instance, the decision to use parboiling can lead to improved nutritional values of the rice by gelatinizing starches and hardening the grains. The table below illustrates the impact of different treatments on rice quality:
| Treatment Method | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|
| Parboiling | Increases nutritional value; reduces breakage |
| White Milling | Enhances polish; improves shelf life |
| Brown Milling | Retains bran; higher fiber content |
By continually refining these approaches and embracing technological advancements, rice processing plants can achieve optimal efficiency, ensuring they meet the ever-growing demands of the market while maintaining excellent quality standards.
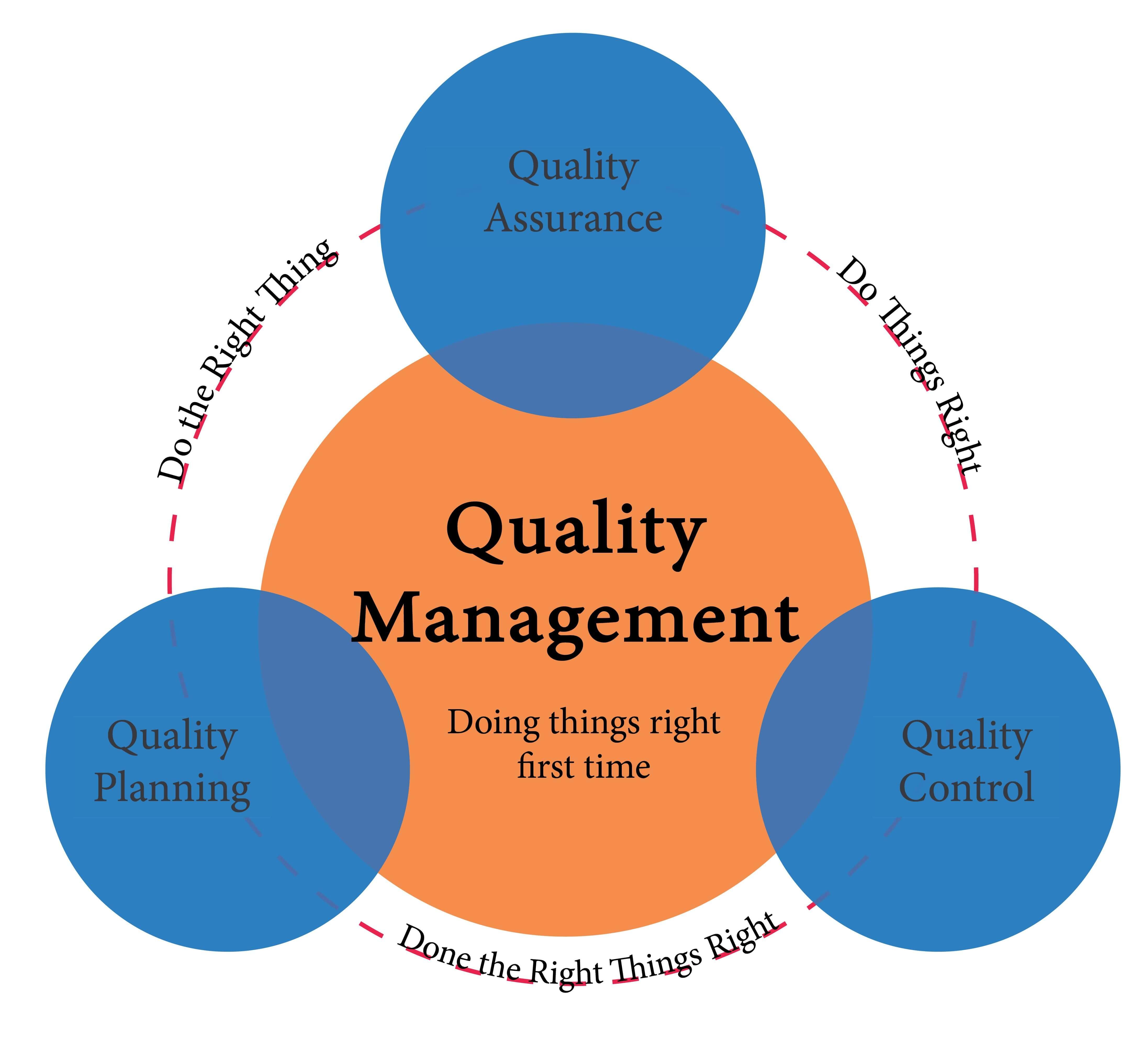
Quality Control in Rice Production: Ensuring Standards from Grain to Pack
In the intricate world of rice milling, maintaining high standards of quality control is paramount. Each stage of the process, from harvesting to packing, requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets both safety and quality benchmarks. A well-structured quality control system involves regular monitoring and testing at various checkpoints. This may include visual inspections of raw grains, moisture analysis, and grading for size and color. Additionally, skilled technicians often conduct sensory evaluations, assessing factors such as taste and aroma, crucial to satisfying consumer preferences. By creating a quality assurance team, plants can implement protocols that govern every aspect of rice production, confirming that they adhere to industry regulations and standards.
Effective quality control also embraces technological innovations. Automated systems are increasingly deployed to monitor conditions and assess product quality in real time. Sensors linked to data analytics platforms continuously track various parameters, providing immediate feedback and enabling prompt adjustments. Quality control measures extend to the packaging stage as well, with safeguards put in place to prevent contamination and ensure that each bag of rice meets aesthetic and functional criteria. To illustrate the impact of a strong quality management system, consider the following breakdown of potential quality indicators in rice production:
| Quality Indicators | Measurement Methods | Standard Values |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Moisture Meter | 12-14% |
| Broken Grains | Visual Inspection | < 5% |
| Foreign Material | Sieving | < 1% |
By integrating these methodologies, rice mills not only uphold product integrity but also foster a culture of continual improvement that benefits both producers and consumers alike.
Sustainable Practices: Eco-Friendly Innovations in Rice Milling Technology
In the pursuit of sustainability, modern rice milling plants are embracing eco-friendly innovations that not only enhance efficiency but also reduce their environmental footprint. These innovations include the adoption of biomass energy systems that utilize rice husks and other by-products as a renewable energy source for milling operations. This shift not only minimizes reliance on fossil fuels but also facilitates a circular economy within farming communities. Further, advanced water recycling technologies are being implemented to optimize water usage, ensuring that the rice milling process consumes significantly less water compared to traditional methods.
Another significant development in this eco-conscious landscape is the introduction of solar-powered milling machines. By harnessing solar energy, these machines contribute to a substantial decrease in greenhouse gas emissions while providing a sustainable solution for milling in remote areas. Furthermore, the integration of automated control systems and smart sensors allows for real-time monitoring of energy and resource consumption, enabling operators to make informed decisions that promote sustainability. As the rice milling sector evolves, these innovations pave the way for a greener future, ensuring that the demands of agriculture are met without compromising the health of our planet.
Key Takeaways
the intricate dance of machinery and skilled hands within a rice mill plant reflects the broader narrative of food production—a story woven with tradition, innovation, and sustainability. As we have journeyed through the various stages of rice processing, from the initial milling to the final packaging, we’ve observed how each component plays a vital role in bringing this staple grain from the field to our tables. Understanding these inner workings not only enriches our appreciation for this essential crop but also highlights the importance of efficient and responsible practices in an industry that feeds billions. As we continue to explore the supporting networks of agriculture and technology, let us remain mindful of the intricate links that connect us all through the humble grain of rice.