In the heart of verdant rice paddies, where the earth meets the sky in a dance of sunlight and shadows, lies a silent but significant revolution—one that transforms humble grains into essential sustenance for millions. The journey of paddy processing plants is a fascinating tale of innovation and tradition, where centuries-old practices intertwine with modern technology to elevate the harvest from field to table. As rice fields sway gently in the breeze, the story of these processing plants unfolds, revealing the intricate processes that ensure quality and efficiency, all while navigating the challenges of sustainability and evolving consumer demands. Join us as we journey into the world of paddy processing, exploring the transformations that occur behind the scenes and shedding light on the vital role these facilities play in feeding a growing global population. Whether you’re a farmer, a consumer, or simply curious about what lies beyond the grain, this exploration will unveil the artistry and science of turning raw paddy into the staple food that sustains us all.
Revolutionizing Efficiency in Paddy Processing Operations
In recent years, the landscape of paddy processing has witnessed a seismic shift, defined by the integration of cutting-edge technology and innovative practices. Modern processing plants are no longer constrained by traditional methods; instead, they have embraced automation, data analytics, and sustainable practices to maximize productivity and reduce waste. Key advancements include:
- Automated Sorting Systems: Utilizing AI-driven technology, these systems ensure each grain meets quality standards, significantly minimizing human error.
- Energy-efficient Machinery: New equipment designed with energy-saving features decreases operational costs and environmental impact.
- Real-time Monitoring: IoT devices provide consistent feedback on the processing stages, allowing for swift adjustments and higher efficiency.
Furthermore, the evolution of paddy processing operations highlights the importance of sustainable practices. Innovations related to waste management—like rice husk gasification—are enabling plants to utilize by-products as renewable energy sources, effectively closing the loop in the production cycle. Transactional efficiencies are bolstered by:
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | Modern Innovations |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Up to 12 hours per batch | Reduced to 6 hours with automation |
| Energy Consumption | High, depending on fuel source | Lower, with efficient machinery |
| Waste Generation | Significant by-products | Recycled into energy and fertilizer |
By shifting towards these innovative solutions, paddy processing plants are not only transforming their operational capacities but are also playing a pivotal role in promoting sustainability within the agricultural sector.
Sustainable Practices: Balancing Output with Environmental Stewardship
In the quest for elevating paddy processing to meet both consumer demands and environmental expectations, plants are increasingly adopting innovative techniques that prioritize sustainability. Through a combination of *advanced technology, resource management*, and *community engagement*, these facilities are transforming the agricultural landscape. Key methods include:
- Waste Reduction: Implementing systems to minimize by-product wastage, turning what was once considered refuse into compost, animal feed, or bioenergy.
- Water Conservation: Utilizing closed-loop systems that recycle water used in processing, significantly reducing overall consumption.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Harnessing solar, wind, or biogas to power operations, diminishing reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, paddy processing plants are also fostering partnerships within the local community to ensure holistic environmental stewardship. By engaging farmers in sustainable agricultural practices, they work towards reducing pesticide use and enhancing soil health, which benefits both crop yields and biodiversity. This collaboration extends to educational initiatives that focus on:
- Training Workshops: Providing hands-on knowledge about eco-friendly farming methods.
- Research Funded Programs: Collaborating with local universities to innovate better practices.
- Community Clean-Up Drives: Organizing efforts to keep local ecosystems free from pollution.
To provide a clearer perspective on the environmental impact, here’s a comparative table of traditional versus sustainable practices in paddy processing:
| Aspect | Traditional Practices | Sustainable Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage | High consumption; often wasteful | Recycling systems in place; conservation-focused |
| Energy Source | Fossil fuel reliance | Incorporation of renewables |
| Waste Management | Landfill disposal | Composting and energy production |
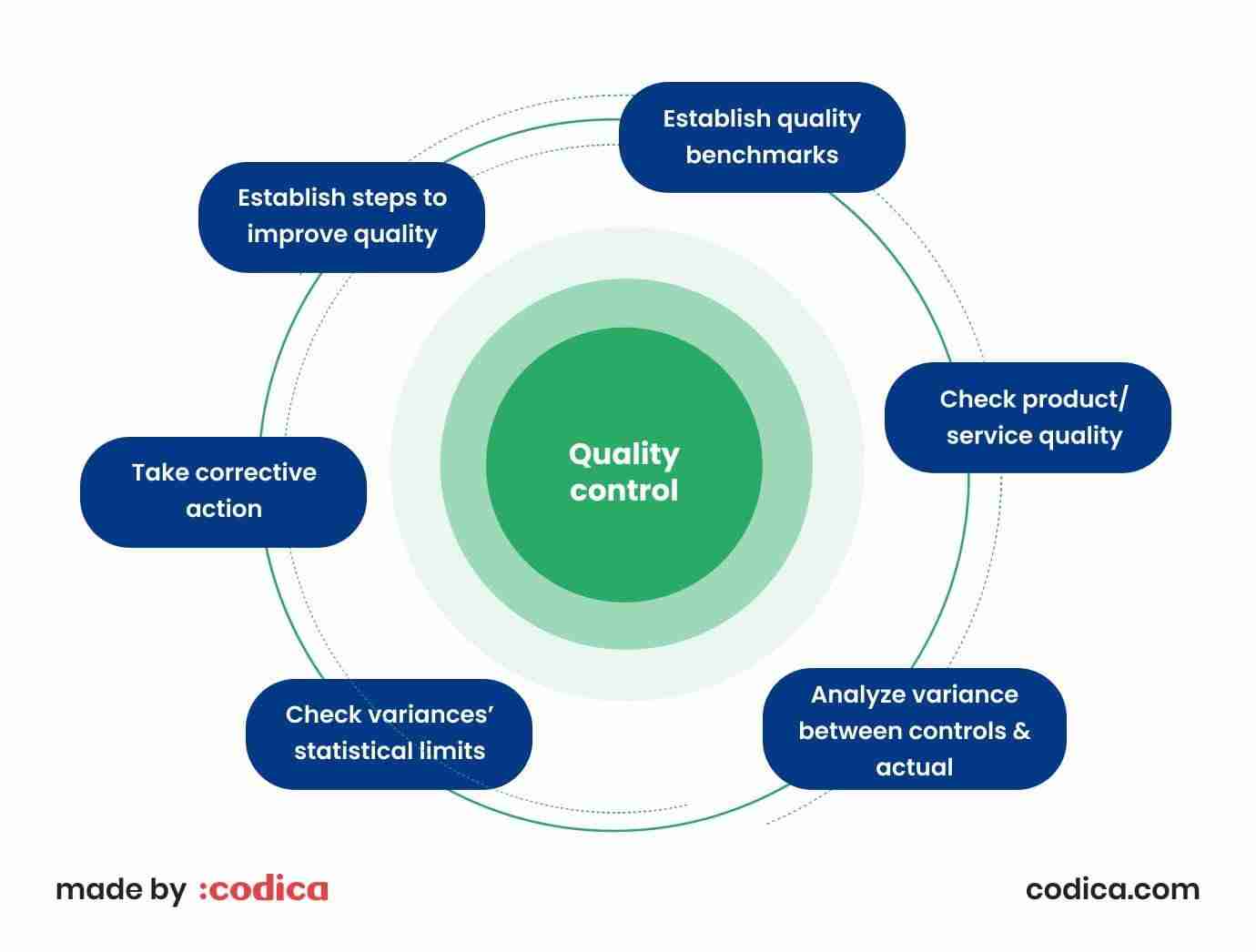
Quality Control Innovations: Ensuring Premium Rice from Field to Fork
In the pursuit of excellence, the journey from paddy to premium rice has undergone a revolutionary transformation, driven by innovations in quality control. At the heart of processing plants, advanced technologies such as machine learning and computer vision are redefining how rice is monitored throughout its journey. Real-time analytics allow for the identification of quality issues at various stages, ensuring that only the finest grains make it to consumers’ tables. The integration of automated sorting machines and sensor technology enhances precision by minimizing human error and ensuring uniformity in grain size and quality.
Furthermore, the implementation of sustainability practices within paddy processing is paving the way for a more responsible approach to rice production. These innovations not only focus on the immediate processing aspects but also encompass a holistic view of resource management. Key features include:
- Water recycling systems that reduce waste during washing stages.
- Energy-efficient machinery that lowers carbon footprints.
- Robust tracking systems for a transparent supply chain from field to fork.
Such advancements are not merely beneficial for quality but also provide a competitive advantage in a global market increasingly focused on sustainability and premium quality. This blend of technology and responsible practices ensures that consumers can enjoy the very best rice, thoughtfully sourced and processed.
Empowering Communities: The Socioeconomic Impact of Modern Processing Technologies
The adoption of modern processing technologies in paddy processing plants significantly uplifts local communities, redefining their socioeconomic landscape. With advanced mechanization and automated systems, these facilities increase efficiency, enabling faster processing times and higher output quality. As a result, farmers benefit from higher profit margins, while also experiencing a reduction in post-harvest losses. This technological shift creates ripple effects throughout the community, fostering job creation and skill development. For instance, local labor markets see a rise in demand for technicians and operators, encouraging training programs and educational initiatives that enhance workforce skills.
Moreover, the enhanced processing techniques contribute to better product quality and sustainability, which in turn attracts regional and international markets. This competitiveness not only elevates the status of local paddy but also strengthens community ties through cooperative initiatives. Consider the following benefits:
- Improved Food Security: By maximizing yield and minimizing waste, communities can ensure a stable supply of rice.
- Environmental Sustainability: Modern technologies often incorporate eco-friendly practices that reduce the carbon footprint of processing.
- Increased Access to Markets: Enhanced quality opens doors to premium pricing and more diverse buyers.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Employment Opportunities | Increased demand for skilled labor in processing. |
| Economic Growth | Enhanced revenue for farmers and local businesses. |
| Community Development | Investments in local infrastructure and services. |
To Wrap It Up
As the sun sets on the fields of golden grains, the journey of paddy continues far beyond the harvest. From the moment the rice is harvested to its transformation into the staple we cherish, every step in the processing plants plays a crucial role in shaping the final product. These facilities, with their intricate machinery and skilled hands, ensure that each grain is polished, sorted, and packaged with the utmost care.
The evolution of paddy processing plants reflects not just advancements in technology but also a deep understanding of sustainability and quality. As we move toward a future where food security is paramount, these plants stand as beacons of innovation, adapting to the challenges of a changing world while preserving the rich heritage of rice cultivation.
In closing, the story of paddy processing is one of resilience and transformation—a testament to the dedication of communities that stand behind this essential crop. As we savor each meal that includes rice, let us remember the journey of these humble grains, from the fields to our tables, and the dedicated processes that transform harvests into nourishment for millions around the globe.