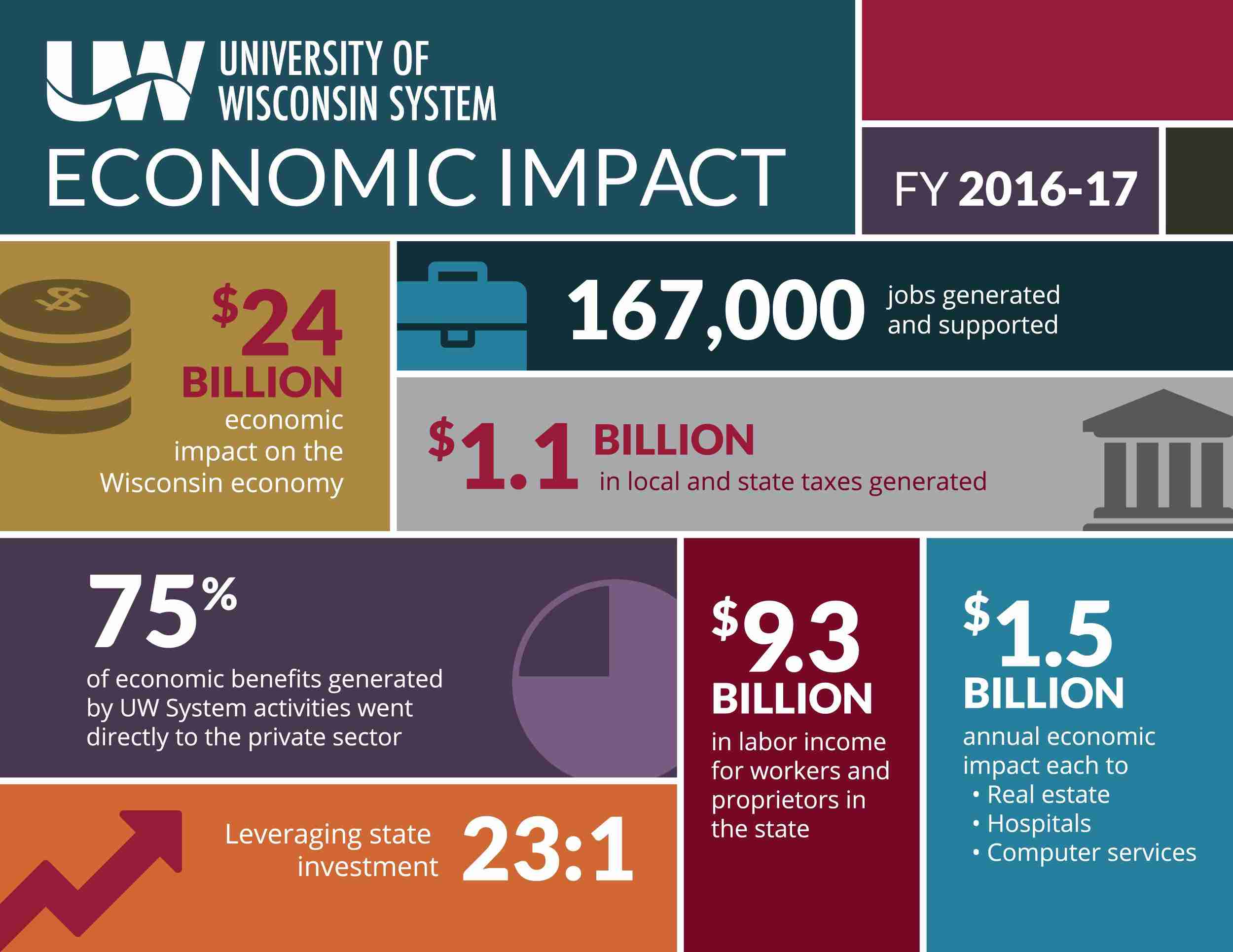
In the heart of agricultural landscapes, where golden fields of rice sway gently in the breeze, a quiet revolution is taking place. The journey from paddy to polished grain is often overlooked, but it’s a transformation laden with significance. Paddy processing units, the unsung heroes of the grain industry, play a pivotal role in this metamorphosis. They not only enhance the quality and yield of rice but also empower farmers, invigorate local economies, and contribute to food security. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of these processing units, exploring how they bridge the gap between harvest and consumption, and ultimately reshape the livelihoods of communities around the globe. As we unpack the layers of this transformation, we will uncover the intricate interplay of technology, tradition, and innovation that drives the paddy processing sector forward.
Understanding the Role of Paddy Processing Units in Agricultural Development
In the landscape of agricultural development, paddy processing units serve as pivotal hubs that not only enhance grain value but also fortify local economies. These facilities are essential for transforming raw paddy into consumable rice, streamlining the process through modern machinery and efficient protocols. By adopting innovative processing techniques, these units deliver several key benefits, which include:
- Increased Grain Quality: Advanced processing improves the taste and texture of rice, making it more appealing to consumers.
- Waste Reduction: Efficient processing minimizes waste, ensuring that most parts of the paddy are utilized, which is vital in sustainable agriculture.
- Job Creation: Local communities benefit from employment opportunities, ranging from skilled positions in maintenance to unskilled labor in production.
Moreover, paddy processing units contribute significantly to agricultural productivity and market access. They act as a bridge between farmers and consumers, transforming paddy into readily available products that cater to diverse market demands. These units empower farmers by offering them more favorable pricing structures due to value addition, thus enhancing their profitability. A glimpse of their impact can be illustrated in the following table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Access | Facilitates connections between smallholder farmers and larger markets. |
| Value Addition | Transforming raw paddy into ready-to-sell rice leads to higher profits. |
| Technological Advancement | Incorporation of modern technologies increases efficiency and reduces manual labor. |
This comprehensive approach to paddy processing underscores its integral role in shaping agricultural futures, enhancing both food security and economic resilience within rural areas. By investing in these processing units, we foster a system that not only uplifts farmers but also prepares communities for sustainable development.
Enhancing Efficiency: Technological Innovations in Grain Processing
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, technological innovations have emerged as game-changers in the realm of grain processing. Modern paddy processing units are pivotal in streamlining operations, enhancing yield quality, and minimizing waste. Automation plays a significant role, integrating advanced machinery such as separators, rice polishers, and de-huskers that work in perfect harmony to produce high-quality rice. With real-time monitoring systems, farmers can now track the entire processing journey, ensuring parameters are optimized, and decisions are data-driven. The use of artificial intelligence to predict machine failures further enhances productivity, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
Additionally, innovations in energy efficiency are transforming how grain processing units operate. By employing renewable energy sources, such as solar or biomass, many facilities have drastically reduced their carbon footprint. This shift not only benefits the environment but also decreases operational costs, ultimately leading to competitive pricing for consumers. The incorporation of smart sensors facilitates continuous feedback on moisture levels and temperature, which are essential for achieving the ideal processing conditions. As a result of these advancements, the entire paddy processing ecosystem is becoming increasingly robust and resilient, capable of meeting the global demand for rice while ensuring sustainability.
| Innovation Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Automation | Improved efficiency and reduced labor costs |
| AI Monitoring | Predictive maintenance for less downtime |
| Renewable Energy | Lower operational costs and reduced carbon footprint |
| Smart Sensors | Optimized processing conditions for quality control |
Economic Benefits: Empowering Local Communities through Paddy Processing
Paddy processing units serve as more than just facilities for transforming rice; they act as crucial economic engines for local communities. By establishing these units, we empower farmers to maximize the value of their crops and enhance their livelihoods. The direct benefits of local processing include:
- Increased Income: Farmers receive better prices for processed rice compared to selling raw paddy.
- Job Creation: Processing units create employment opportunities, not only in the plants but also in ancillary services.
- Enhanced Skills: Workers gain essential agricultural processing skills that can lead to further employment opportunities or entrepreneurship.
Moreover, the establishment of paddy processing facilities fosters a sense of community and collaboration among farmers. They can engage in cooperative models, sharing resources and knowledge, which strengthens their collective bargaining power. This unity translates into several economic advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Access to Markets | Processed rice can be marketed more effectively, reaching broader consumer bases. |
| Value Addition | By processing their paddy, farmers can diversify their products, leading to increased sales and revenue. |
| Community Resilience | Empowered farmers and skilled workers create a robust local economy less susceptible to external shocks. |
Sustainability Practices: Balancing Production with Environmental Stewardship
In the realm of agricultural processing, especially within paddy processing units, the integration of sustainability practices has become paramount. These facilities are increasingly recognizing the delicate balance between production efficiency and environmental stewardship. Implementing strategies such as water conservation, energy efficiency, and waste management not only aids in reducing the ecological footprint but also ensures a more resilient operational model. By reusing water in the milling process and investing in renewable energy sources, these units can drastically lower their environmental impact while maintaining high production levels.
Moreover, the adoption of eco-friendly technologies has paved the way for innovative practices that enhance both output and sustainability. Some notable practices include:
- Biomass Utilization: Converting husk and straw into energy or organic fertilizer not only minimizes waste but also provides additional revenue streams.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing data-driven approaches to optimize planting and harvesting leads to reduced input usage and higher yields.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with local farmers ensures sustainable sourcing of paddy and fosters a stronger community commitment to environmental health.
To further illustrate the practical impacts of these practices, consider the following table showcasing key performance indicators (KPIs) for sustainability in paddy processing units:
| Sustainability Initiative | Impact on Production | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Water Reuse Systems | Reduces water usage by 30% | Minimizes water pollution |
| Solar Energy Integration | Increases energy efficiency by 25% | Lower greenhouse gas emissions |
| Effluent Treatment Plants | Enhances process sustainability | Protects local water sources |
Final Thoughts
In the intricate dance of agriculture and industry, the role of paddy processing units emerges as a critical pivot, transforming raw grain into staple foods that sustain millions. As we peel back the layers of this transformation, it becomes clear that these units do more than just process rice; they connect rural communities to global markets, preserve traditional practices, and drive economic growth. The meticulous art of milling, sorting, and packaging not only enhances the quality of the grain but also opens doors to innovation in farming and beyond.
As we stand at the crossroads of tradition and modernization, the impact of paddy processing units extends far beyond the borders of the fields. They symbolize resilience in the face of change, adaptability in the face of challenges, and a vision for a sustainable agricultural future. This transformation breathes new life into local economies, empowers farmers, and enables consumers to access quality food.
In this journey of grain, from paddy fields to our plates, we witness a story of ambition and progress. As we continue to explore the implications of these processing units, it invites us to consider: how can we harness this transformation to cultivate a future where food systems are equitable, efficient, and environmentally sound? The answers lie in the synergy of innovation, community engagement, and a shared commitment to nurturing the very essence of our agricultural heritage. The journey of paddy processing is just beginning, and its potential is as vast as the fields from which it comes.