In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and efficiency, the journey from grain to plate has never been more essential to our understanding of food production. At the heart of this journey lies the humble paddy, a staple for billions and a cornerstone of agricultural economies. But what happens after the harvest? How do those golden grains transform into the rice that fills our bowls and nourishes our families? In this article, we will explore the intricate and often overlooked paddy processing journey, illuminating the steps and innovations that streamline this vital process. From the lush fields of rice paddies to the bustling kitchens where meals are prepared, we will uncover the transformative path that reinforces the connection between farm and table, celebrating the processes that make this staple food accessible and delicious. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of grain processing and discover the dedication, technology, and tradition behind bringing rice from swathes of green to plates around the globe.
Understanding the Paddy Processing Stages for Optimal Yield
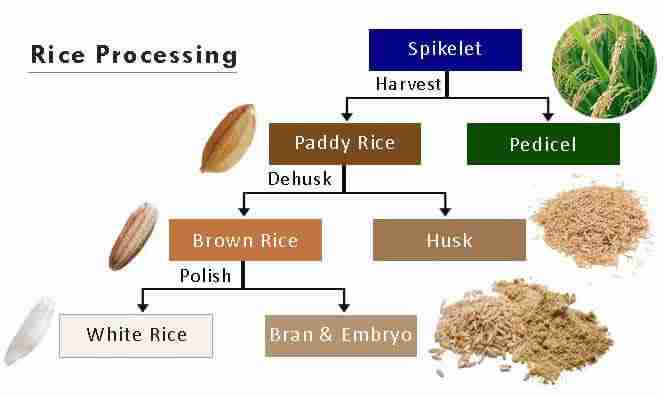
Processing paddy involves several critical stages, each designed to enhance the quality and yield of the final product. Initially, harvesting is crucial, where the paddy is cut and collected, typically at its peak ripeness to ensure maximum grain retention. Next, the harvested paddy undergoes threshing, where grains are separated from their husks. This step is vital as it sets the stage for the subsequent drying process, which is essential to reduce moisture levels and prevent spoilage. Cleaning follows, involving the removal of impurities such as dirt, stones, and broken grains, ensuring only quality paddy proceeds to the next phases.
Once cleaned, the paddy is subjected to milling, where it is husked and polished to convert it into white rice or other forms, depending on market demands. During this stage, it’s important to monitor the breakage rates—excessive breakage leads to lower quality rice and economic losses. After milling, the rice may enter grading, where it is sorted according to size and quality, further enhancing marketability. the processed rice undergoes packaging, ensuring it is sealed appropriately to retain freshness. This comprehensive understanding of each stage not only helps producers streamline their operations but also maximizes yield quality, encapsulating the journey from grain to plate.
| Processing Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collecting the ripe paddy at peak maturity. |
| Threshing | Separating grains from husks through mechanical means. |
| Drying | Reducing moisture content to prevent spoilage. |
| Cleaning | Removing dirt and foreign materials from the grains. |
| Milling | Husking and polishing to produce white rice. |
| Grading | Sorting rice based on size and quality. |
| Packaging | Sealing the rice to maintain freshness. |
Innovative Technologies Transforming Grain Processing Efficiency
The advent of cutting-edge technologies in grain processing has revolutionized the industry, significantly enhancing efficiency from the initial paddy harvesting to the final product on our plates. Automated sorting systems, equipped with advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms, now enable producers to meticulously classify grains based on quality, moisture levels, and size. This not only minimizes human error but also reduces labor costs and enhances the speed of processing. Additionally, drone technology is making waves in monitoring fields—providing real-time data about crop health, moisture, and yield potential, thus allowing farmers to make informed decisions about when to harvest for optimal quality.
Moreover, innovative milling technologies have emerged that utilize high-efficiency machinery designed to maximize output while lowering energy consumption. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices allows for smart processing plants, where machinery communicates seamlessly to optimize operations continuously. For example, predictive maintenance helps in foreseeing equipment failures before they occur, ensuring smooth production flows. To illustrate these advancements, consider the following table that summarizes key innovations and their impacts:
| Innovation | Impact on Processing |
|---|---|
| Automated Sorting Systems | – Improves quality control and reduces processing time |
| Drone Technology | – Real-time monitoring and data-driven decisions |
| High-Efficiency Milling | - Increases output while decreasing energy use |
| IoT Devices | – Enhances operational efficiency through predictive maintenance |
Sustainable Practices in Paddy Handling and Distribution
Ensuring sustainable practices in the handling and distribution of paddy is essential for minimizing environmental impact while maximizing efficiency. Innovative technologies such as moisture meters and automated sorting machines help maintain the quality of paddy through precision monitoring and sorting. By implementing these tools, we can reduce waste and enhance yield, ultimately resulting in a fresher, more desirable product for consumers. Additionally, collaborative efforts among farmers, processors, and distributors can promote eco-friendly logistics that utilize fewer resources, such as opting for local transportation methods to decrease carbon footprints.
The integration of sustainable packaging solutions also plays a crucial role in reducing environmental consequences. By using biodegradable or recyclable materials, the industry can significantly decrease plastic usage, promoting a cleaner ecosystem. Moreover, the adoption of closed-loop systems in processing, where byproducts are repurposed for other uses, reflects a commitment to circular economy principles. To illustrate the impact of these methods, consider the following table showcasing potential benefits:
| Practice | Environmental Impact | Economic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Monitoring | Reduces spoilage | Increases product value |
| Local Distribution | Decreases emissions | Supports local economy |
| Biodegradable Packaging | Reduces plastic waste | Enhances brand image |
Enhancing Quality Assurance from Farm to Fork
In the intricate journey from paddy to plate, ensuring excellence at every stage is paramount for maintaining the integrity of food quality. Building a robust framework for quality assurance begins right at the farm, where sustainable agriculture practices come into play. This involves:
- Soil Health Monitoring: Regular assessments of soil quality promote nutrient-rich growth.
- Water Usage Regulations: Efficient irrigation techniques minimize waste and improve crop yield.
- Pesticide Control: Implementing natural pest control methods reduces chemical exposure, enhancing food safety.
As the paddy is processed, the emphasis on quality control measures remains crucial. Kosher certification, organic labeling, and traceability systems are essential components that ensure transparency throughout the supply chain. Key aspects include:
| Quality Assurance Component | Impact on Food Safety |
|---|---|
| Regular Sampling and Testing | Detects contaminants early, preventing public health issues. |
| Supplier Audits | Ensures compliance with safety standards at all levels. |
| Consumer Feedback Mechanisms | Informs producers about quality perceptions, driving improvements. |
Concluding Remarks
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of the paddy processing journey, it becomes clear that the path from grain to plate is a complex and intricate tapestry woven from nature, technology, and human effort. Each step, from harvesting the golden ears of rice to the meticulous milling and distribution processes, exemplifies a delicate balance of tradition and innovation.
This journey not only underscores the importance of efficient practices in meeting the demands of a growing global population but also highlights the significance of sustainability in preserving the very resources that nourish us. As consumers, understanding this process empowers us to appreciate the food on our plates and the stories behind them.
As we look toward the future, let us continue to support efforts that advocate for sustainable practices and innovations in the paddy processing sector. The journey from grain to plate is not merely an agricultural movement; it is an invitation to engage with the food systems that sustain us and the farmers who dedicate their lives to bringing nourishment to our tables. In every bite of rice, there lies a journey, and it is one that we should cherish and respect.