In the heart of rural landscapes, where golden fields sway gently under the caress of the wind, lies a bustling hub of activity that transforms humble grains into vital sustenance for millions. The paddy processing unit, often overlooked yet critical to our agricultural and culinary tapestry, plays a pivotal role in this transformation. Here, science meets tradition as raw paddy undergoes meticulous steps of milling, polishing, and packaging, evolving into the polished rice that graces our tables. This article takes you behind the scenes into the intricate world of paddy processing, exploring the technology, labor, and environmental considerations that shape this essential industry. Join us as we uncover the journey of grains from field to fork, illuminating the unsung heroes who toil day in and day out to ensure that the fruits of the earth reach our plates.
Understanding the Paddy Processing Journey from Field to Table
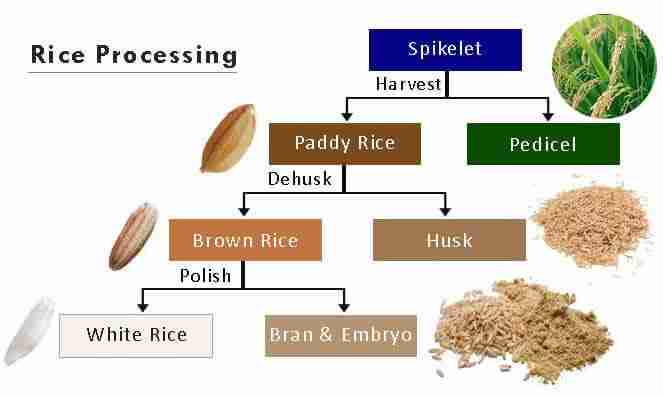
The journey of paddy from the lush green fields to our dining tables is a meticulous process that transforms raw grains into the staple food we cherish. Initially, after harvest, the paddy is delivered to a processing unit where it undergoes several stages. Each step is crucial for ensuring the quality and safety of the rice we consume. Some of the key stages include:
- Drying: Freshly harvested paddy grains are dried to reduce moisture content, preventing spoilage.
- Hulling: The outer husk is removed using hulling machines, resulting in brown rice.
- Milling: Brown rice is polished to produce white rice, enhancing its texture and flavor.
- Grading: The rice is sorted based on size, color, and quality to ensure uniformity.
Following the processing stages, rice undergoes rigorous quality checks to meet standards before packaging. The final product is then distributed to various markets, making its way to homes and restaurants. Here’s a brief overview of the rice quality grading process:
| Grade | Description | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Premium | Highest quality; long grains with minimal broken rice | Fine dining, gourmet dishes |
| Standard | Good quality; some broken grains | Everyday meals, home cooking |
| Base | Contains higher levels of broken rice and impurities | Rice flour, industrial use |
Innovative Techniques in Milling and Post-Harvest Processing
In the intricate world of grain processing, innovative techniques are essential for maximizing efficiency and quality. Milling technology has significantly advanced in recent years, shifting towards precision equipment that minimizes waste and enhances the nutritional value of grains. Modern multi-stage milling systems employ a combination of optical sorting and high-precision polishing mechanisms, ensuring that only premium grains make it to the final product. These systems can separate grain based on size, weight, and even color, leading to a more refined output. Innovations such as vertical milling machines and dehuskers also play a significant role, allowing for superior extraction rates and reducing the wear and tear on machinery.
The post-harvest processing landscape is also witnessing groundbreaking advancements, particularly in drying and storage practices. With the advent of solar-powered dryers and controlled atmosphere storage facilities, farmers can now extend the shelf life of their products while preserving their quality. By employing smart technology in monitoring temperature and humidity levels, it becomes easier to avert spoilage and maintain grain integrity. Further, embodiments of AI-driven analytics guide the storage processes by predicting optimal conditions, thereby safeguarding a year’s worth of harvest. Collectively, these techniques not only improve product quality but also enhance economic stability for smallholder farmers.
Quality Control and Sustainability: Best Practices for Paddy Processing
In the realm of paddy processing, maintaining quality control is essential not only for ensuring the integrity of the product but also for promoting sustainability within the industry. Implementing best practices can significantly enhance both the quality of processed rice and the environmental footprint of production. Some strategies include:
- Regular Quality Assessment: Establish a routine inspection schedule that assesses grain quality at various stages of processing, from de-husking to polishing.
- Adoption of Eco-Friendly Technologies: Utilize energy-efficient machinery and renewable energy sources to minimize resource consumption and carbon emissions.
- Water Management Practices: Implement water recycling systems in the processing unit to reduce waste and promote efficient water use throughout the production cycle.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of sustainability goes hand-in-hand with quality control in the paddy processing industry. Encouraging collaboration among stakeholders, such as farmers and suppliers, can lead to shared knowledge about sustainable practices. Key areas of focus should include:
- Educational Programs: Provide training sessions for workers on the importance of sustainable methods and how to implement them effectively.
- Organic Certifications: Aim for certifications that highlight eco-friendly practices, enhancing marketability and consumer trust.
- Waste Minimization: Emphasize the recycling and repurposing of by-products from processing, creating additional revenue streams while reducing waste.
Future Trends in Grain Transformation and Market Opportunities
As the global demand for sustainable and nutritious food sources rises, the transformation of grains, particularly through advanced paddy processing techniques, opens new avenues for innovation in the agricultural sector. Emerging technologies are poised to reshape the landscape of grain processing, leading to more efficient and environmentally friendly practices. Among the anticipated trends are:
- Automation and Robotics: These technologies promise enhanced efficiency and reduced labor costs, enabling facilities to scale operations swiftly.
- Precision Processing: Utilizing data analytics to optimize each stage of paddy processing can minimize waste and maximize yield.
- Biotechnology Integration: Innovations in genetic engineering may lead to crops with higher resistance to pests and better nutritional profiles.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, such as water recycling and zero waste processing, will likely become prerequisites for competitive advantage.
Alongside these transformative technologies, the market opportunities for value-added products derived from grains are expanding. With consumers becoming increasingly health-conscious, there’s a growing interest in functional foods made from carefully processed grains. This potential can be seen in the burgeoning areas of:
- Plant-Based Protein: Grains are being increasingly utilized as plant protein sources, catering to the vegetarian and vegan market segments.
- Gluten-Free Alternatives: The rise in gluten intolerance awareness has spawned innovation in gluten-free grain product lines.
- Ready-to-Eat Meal Solutions: Convenience continues to drive demand for processed grains in pre-packaged meals, ideal for busy lifestyles.
- Health Supplements: Fortified grains with added vitamins and minerals are gaining traction, appealing to the nutraceutical market.
| Opportunity | Market Growth (%) | Key Players |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Protein | 25 | Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods |
| Gluten-Free Products | 20 | Bob’s Red Mill, Schär |
| Ready-to-Eat Meals | 15 | Kraft Heinz, Nestlé |
| Health Supplements | 30 | Garden of Life, Nature’s Way |
Concluding Remarks
As we conclude our journey through the intricate world of paddy processing, it becomes clear that this seemingly simple grain holds the key to a multifaceted industry. From the careful cultivation of paddy fields to the hum of machinery in processing units, every step is a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. The transformation of grains is more than just a mechanical process; it’s a blend of tradition and technology, art and science.
As we reflect on the vital role these processing units play in ensuring food security and economic stability, we recognize the dedication of the individuals who work tirelessly behind the scenes. They not only safeguard the quality of our staple food but also contribute to a sustainable future for agriculture.
In a world where every grain counts, understanding the journey of paddy from field to table is more important than ever. Let us carry this newfound appreciation forward, celebrating the invisible threads that connect us to the food we eat. As the sun sets over the paddy fields, may we continue to explore the innovations that lie within this essential crop and honor the transformation it undergoes, enriching our diets and our lives.