Transforming Rice: The Essential Guide to Paddy Processing Units
In the heart of agricultural innovation lies a humble yet vital staple – rice. Cultivated across diverse landscapes, this grain is far more than a mere staple food; it is a cultural cornerstone and a source of livelihood for millions. However, the journey from paddy field to table is complex, involving intricate processes that refine raw grains into the polished products we know and love. Enter the paddy processing unit, a transformative hub that captures the essence of this journey. In this guide, we will explore the critical role of these units in the rice supply chain, delving into the technologies, techniques, and best practices that drive efficiency and sustainability. Whether you are a farmer, entrepreneur, or simply an enthusiast of the culinary arts, understanding the intricacies of paddy processing is essential for appreciating the rice that graces our plates. Join us as we uncover the fascinating world of rice transformation, where tradition meets innovation in the pursuit of quality and nourishment.
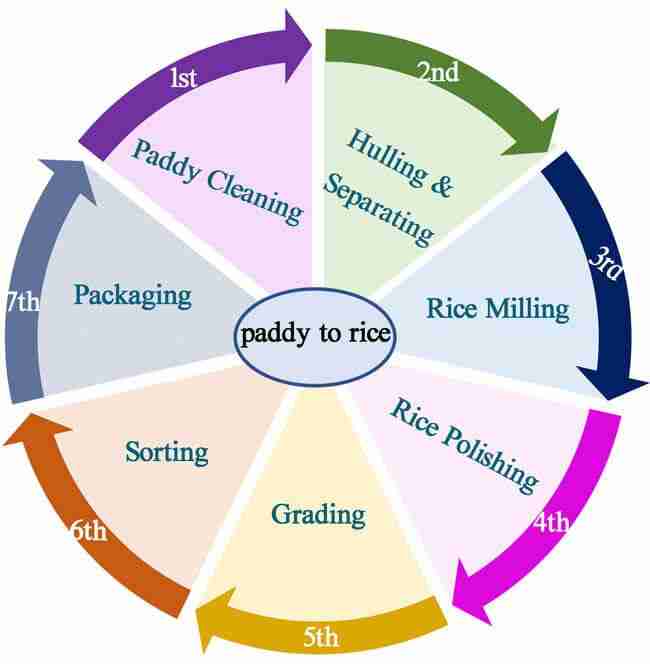
Understanding the Paddy Processing Cycle and Its Importance
The paddy processing cycle is vital in transforming raw paddy into the white rice that graces our tables. This intricate process begins with the harvesting of paddy, where the grains are collected and then dried to reduce moisture content—a critical step that prevents spoilage. Once dried, the paddy is subjected to milling, where husks are removed, and the grains are polished. This phase not only enhances the rice’s appearance but also improves its shelf life. The significance of each stage in the cycle cannot be overstated, as it directly affects the quality, yield, and marketability of the final product.
Moreover, the efficiency of paddy processing units plays a crucial role in the agricultural economy. These units are equipped with various machines that streamline the processing cycle, ensuring maximum output from minimal input. The importance of *technological advancement* and *proper machinery* includes:
- Increased Efficiency: Reduces time and labor.
- Higher Quality: Produces better-grade rice with fewer impurities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Optimizes resource usage and reduces waste.
In addition, implementing sustainable practices in these units can significantly enhance environmental conservation. Below is a simple table showcasing the key elements involved in the paddy processing cycle:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collecting and gathering harvested paddy. |
| Drying | Reducing moisture content for preservation. |
| Milling | Removing husks and polishing rice grains. |
Key Technologies and Machinery in Rice Processing Units
In the intricate realm of rice processing, several key technologies and machines play pivotal roles in transforming harvested paddy into the polished grains that line our shelves. Modern milling equipment enhances the efficiency and quality of processing, ensuring minimal loss and maximum yield. Essential appliances include:
- Paddy Separator: This machine segregates paddy from brown rice, ensuring optimal quality before further processing.
- Rice Whitener: Designed to remove the outer bran layer, it polishes the rice grain while preserving its nutritional value.
- Grading Machines: These devices classify rice based on size and quality, facilitating efficient packaging and sale.
Additionally, some technological advancements streamline operations in processing units, promoting automation and data-driven decision-making. For instance, automated weight and packaging systems increase efficiency and accuracy in packaging, while sensor-based quality control ensures that only the finest grains are delivered to consumers. Here’s a glance at how these technologies enhance rice processing efficiency:
| Technology | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Packaging | Weighs and packages rice | Increases speed and reduces human error |
| Sensor Quality Control | Analyzes grain quality | Ensures premium products for consumers |
| Energy-Efficient Dryers | Removes moisture from grains | Prevents spoilage and maintains quality |
Best Practices for Enhancing Efficiency and Quality in Rice Transformation
Maximizing efficiency in rice transformation requires a strategic approach that encompasses both technology and management practices. To streamline operations, consider implementing modern milling techniques that not only reduce waste but also enhance the quality of the final product. Engaging in regular machinery maintenance ensures optimal performance and prolongs the lifespan of your equipment. Additionally, focusing on operator training helps develop a skilled workforce capable of identifying potential issues before they escalate, thus maintaining productivity levels. Monitoring workflow and implementing systematic quality checks at various stages can help in achieving a consistent output, while also ensuring adherence to food safety standards.
Integrating sustainability measures into rice processing units presents another avenue for improvement. By adopting energy-efficient technologies such as solar-powered drying systems, operations can significantly cut down on energy costs while contributing to environmental preservation. Exploring the use of biowaste management methods can also create a circular economy within the unit, where by-products from rice processing are repurposed for other uses, such as animal feed or organic fertilizers. Formulating partnerships with local farmers can further enhance supply chain efficiency, ensuring a steady flow of quality paddy while supporting the local economy.
Sustainability in Paddy Processing: Strategies for a Greener Future
In the quest for a more sustainable approach to rice production, paddy processing units are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices. By implementing state-of-the-art technologies and adopting innovative methodologies, these facilities can significantly reduce their carbon footprints. Not only do these strategies yield environmental benefits, but they also enhance operational efficiency, ultimately contributing to greater economic viability. Key strategies for fostering sustainability include:
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power to minimize reliance on fossil fuels.
- Waste Management: Implementing systems for recycling by-products such as husks and bran, turning waste into valuable resources like biofuel or animal feed.
- Water Conservation: Employing advanced irrigation techniques and water recycling systems to reduce water consumption during processing.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Transitioning to biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials that reduce landfill impact.
Moreover, collaboration with local farmers and communities can enhance sustainability initiatives in paddy processing. By fostering relationships that prioritize sustainable agricultural practices, processing units can benefit from a more resilient supply chain. This collaborative approach can be supported through programs that educate farmers on organic farming techniques and soil health. A concise overview of sustainability metrics in paddy processing can also be displayed in a tabular format, illustrating the impact of these strategies:
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 20% reduction in energy costs |
| Waste Management | 50% of by-products recycled |
| Water Conservation | 30% reduction in water usage |
| Eco-Friendly Packaging | 80% less plastic waste |
To Wrap It Up
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of “Transforming Rice: The Essential Guide to Paddy Processing Units,” it becomes clear that the journey from paddy to polished grain is a fascinating blend of tradition, innovation, and sustainability. The paddy processing unit stands as a bridge between the farmer’s toil and the consumer’s table, encapsulating stories of agrarian dedication and technological evolution.
With advancements in processing techniques and a growing emphasis on eco-friendly practices, these units are not just processing facilities; they are integral players in the global food security narrative. Their role will only expand as we navigate the challenges of climate change and the demands of a burgeoning population.
As we’ve seen, the future of rice processing is ripe with potential—whether through the adoption of modern machinery, enhanced quality control measures, or sustainable practices that honor both the environment and the communities involved. We hope this guide serves as a valuable resource, igniting inspiration and informing decisions in the ever-evolving landscape of rice processing.
Join us in championing the rice industry, appreciating its complexities, and fostering innovations that celebrate this staple food’s journey from field to table. So, let’s continue to explore, learn, and transform—one grain at a time.