Unveiling the Journey: Inside a Modern Rice Processing Plant
In the heart of agricultural innovation, where tradition meets technology, lies a fascinating world often overlooked: the rice processing plant. This bustling hub of activity takes the humble grain, treasured since ancient times, and transforms it into various forms that grace our tables. Yet, what happens behind the scenes often remains shrouded in mystery. In this article, we embark on a journey through the intricate processes and advanced machinery that breathe life into rice, ensuring it reaches consumers in its finest form. Join us as we explore the stages of production, the meticulous care invested in quality control, and the sustainable practices shaping the future of rice processing. From the sound of machinery whirring to the scent of freshly milled rice, discover the story of this staple food as it travels from field to fork, revealing the complexities of a modern industry dedicated to nourishing millions.
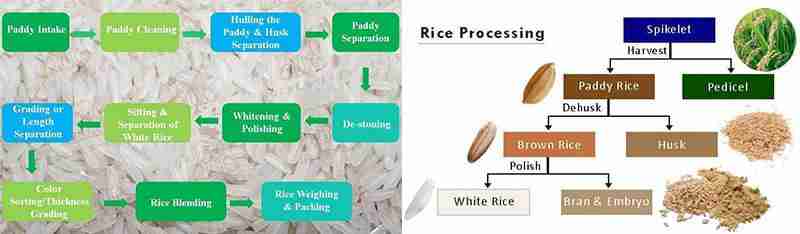
Understanding the Workflow: Steps in Rice Processing from Field to Table
The journey of rice from field to table is a meticulous process that encompasses several critical stages within a modern processing plant. Once harvested, the rice undergoes initial drying to reduce moisture content, a crucial step that prevents spoilage. Following this, the rice is subjected to cleaning, where foreign materials like stones, dirt, and other contaminants are removed through a series of advanced machines. This ensures that only the purest grains move forward. After cleaning, the brown rice is produced by removing the inedible outer layers, but from here, we can take different roads—milling separates the bran and germ from the endosperm, creating either white rice, polished and ready for cooking, or parboiled rice, which maintains nutritional value by steam-processing before milling. The choice of method reflects consumer preferences and culinary needs.
Once the rice is milled, it moves on to quality inspection, where samples are tested for grain size, color, and texture. Modern processing plants utilize cutting-edge technology to ensure only the highest quality rice reaches the market. This is followed by packaging, where rice is stored in moisture-proof bags or containers to extend shelf life and ensure freshness. Ultimately, the finished product is distributed to wholesalers, retailers, and even exported globally, showcasing the efficiency and sophistication of modern agricultural practices. Here’s a simple breakdown of the essential stages involved in rice processing:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collection of matured rice plants from the fields. |
| Drying | Reducing moisture to prevent spoilage. |
| Cleaning | Removing impurities and foreign materials. |
| Milling | Separating the edible rice grain from the husk. |
| Quality Control | Testing for consistency and quality parameters. |
| Packaging | Sealing and preparing rice for distribution. |
Technological Innovations: Modern Machinery Transforming Rice Production
The integration of cutting-edge technologies in rice production has revolutionized the efficiency and effectiveness of processing plants worldwide. Modern machinery has replaced traditional methods, leading to higher yield and quality in every step of the production chain. For instance, automated milling systems utilize advanced sensors and controls to ensure precision and consistency, significantly reducing human error. With the incorporation of AI-driven analytics, farmers and processors now gain real-time insights into operations, optimizing everything from the water used for irrigation to the timing of harvests.
Manual labor has also been transformed with the introduction of robotics and automated equipment. Not only do these innovations decrease the workload on workers, they also enhance productivity and safety. Some key technologies in this movement include:
- Rice Grading Machines: These utilize optical sorting to separate high-quality grains from inferior ones swiftly.
- Continuous Dryers: With advanced thermodynamics, these dryers maintain ideal conditions to prevent loss of quality.
- Smart Packing Systems: Equipped with high-speed technology, ensuring that processed rice is packed efficiently for distribution.
The impact of these technologies is not just limited to efficiency; they also promote sustainable practices, ensuring that rice production meets growing global demands without compromising environmental integrity.
Quality Control Measures: Ensuring Purity and Consistency in Rice Products
The journey of rice from field to table encapsulates a meticulous process where quality control measures play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the end product. Each stage of production, from harvesting to packaging, integrates rigorous protocols designed to ensure both purity and consistency. Innovative technologies now complement traditional practices, offering solutions like real-time monitoring systems that detect impurities at various points in the processing chain. Through these advanced systems, rice grains undergo several tests that check for quality indicators such as moisture content, broken grains, and foreign matter, ensuring that only the best make it to market.
In addition to technological advancements, human expertise remains critical in the quality assurance process. Trained professionals conduct detailed inspections, employing a strict framework that encompasses several key aspects:
- Visual Inspection: Regular checks for color and size uniformity.
- Laboratory Testing: Comprehensive analysis for chemical residues and contaminants.
- Sampling Techniques: Random sampling from batches to ascertain quality consistency.
The integration of these components forms a comprehensive approach to quality control that not only enhances consumer trust but also elevates the standards within the rice industry. A commitment to excellence is evident in the final product, ensuring that each grain meets the highest expectations.
Sustainability Practices: Environmental Considerations in Rice Processing Operations
In the quest for sustainable rice processing, modern facilities have adopted innovative practices that address environmental concerns while maximizing efficiency. The integration of energy-efficient machinery is at the core of these operations, significantly reducing energy consumption throughout the rice milling process. Additionally, many plants are turning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and biomass, to power their operations. By harnessing these resources, plants not only minimize their carbon footprint but also contribute to local energy initiatives. Furthermore, initiatives aimed at minimizing water usage are becoming critical, with advanced water recycling systems enabling facilities to reuse water in various processing stages.
Another critical aspect of sustainability in rice processing is the management of by-products. Instead of discarding rice husks, modern processing plants are capitalizing on these by-products for multiple applications. For example:
- Bioenergy production: Rice husks can be transformed into biofuel, offering an alternative energy source.
- Animal feed: Ground rice husks serve as a nutritious feed additive, promoting sustainable livestock practices.
- Soil amendment: Incorporating rice husks into soil enhances its structure and nutrient content, bolstering agricultural productivity.
Furthermore, the implementation of strict waste management practices ensures that any by-products are handled and processed responsibly, reducing overall waste output. Below is a concise look at some key sustainability metrics vital to rice processing operations:
| Sustainability Metrics | Current Status | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption (kWh/ton) | 80 | 60 |
| Water Usage (liters/ton) | 200 | 150 |
| Waste Recycled (%) | 70 | 90 |
The Way Forward
As we conclude our exploration of the modern rice processing plant, we’ve uncovered the intricate dance of technology and tradition that transforms a humble grain into a staple enjoyed by billions. From the husking and milling stages to the meticulous quality checks, each step in the process reflects the dedication to efficiency and sustainability within the industry. As rice continues to play a vital role in global food systems, understanding the dynamics of its processing journey not only deepens our appreciation for this essential crop but also highlights the innovations forging a path toward a more sustainable future.
In revealing the journey of rice from field to table, we invite you to consider the stories behind the grains on your plate—the laborers, the machines, and the processes that ensure quality and nourishment. As we look ahead, let us celebrate the advancements in rice processing while remaining mindful of the traditions that have sustained this crop for centuries. With every grain, we become part of a larger narrative that connects cultures, communities, and generations.