Unlocking the Grain: A Deep Dive into Rice Milling Units
In the sprawling fields of emerald green, golden grains sway gently in the breeze, each one holding the promise of sustenance and nourishment for millions around the globe. Rice, a staple food for over half of humanity, has a journey that stretches far beyond its humble beginnings in a paddy. At the heart of this journey lies the intricate process of milling, where raw paddy transforms into the polished grains adorning our plates. But what goes on inside a rice milling unit, those often-overlooked hubs of innovation and efficiency? This article embarks on an enlightening exploration of rice milling units, unveiling the technologies that refine this essential commodity, the challenges they face, and their pivotal role in the agricultural landscape. Join us as we unlock the grain and discover the secrets of this vital link in the food production chain.
Understanding the Rice Milling Process and Its Importance
The rice milling process is a meticulous journey that transforms paddy into the white grains that grace our plates, each step vital for ensuring quality and maximizing yield. Initially, paddy is harvested and then subjected to a series of operations including cleaning, hulling, and polishing. During cleaning, impurities such as stones, dust, and debris are removed to ensure that only the best quality grains proceed. Hulling involves the removal of the outer husk, followed by the crucial polishing stage, where the rice is buffed to achieve that soft, shiny appearance. These processes, while seemingly simple, require precision to preserve the nutritional value of the grains while enhancing their aesthetic appeal.
Understanding the intricacies of these operations unveils the importance of rice milling units not just in local economies, but also in fulfilling global food supply needs. Efficient rice milling enhances shelf life, reduces waste, and promotes consumer accessibility, making it a cornerstone of the agricultural industry. The relationship between efficient milling processes and elevated market prices creates a positive feedback loop, benefiting both farmers and consumers. Below is a brief comparison of conventional and modern milling techniques:
| Feature | Conventional Milling | Modern Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Nutritional Preservation | Moderate | Optimal |
| Technology Use | Minimal | Advanced |
| Cost of Operation | Higher | Lower |
Embracing modern milling technologies is not just about coping with demand; it also reflects a commitment to sustainability and food security. By investing in advanced machinery and techniques, rice milling units can play a pivotal role in minimizing environmental impact while maximizing productivity—making them indispensable in our global agricultural framework.
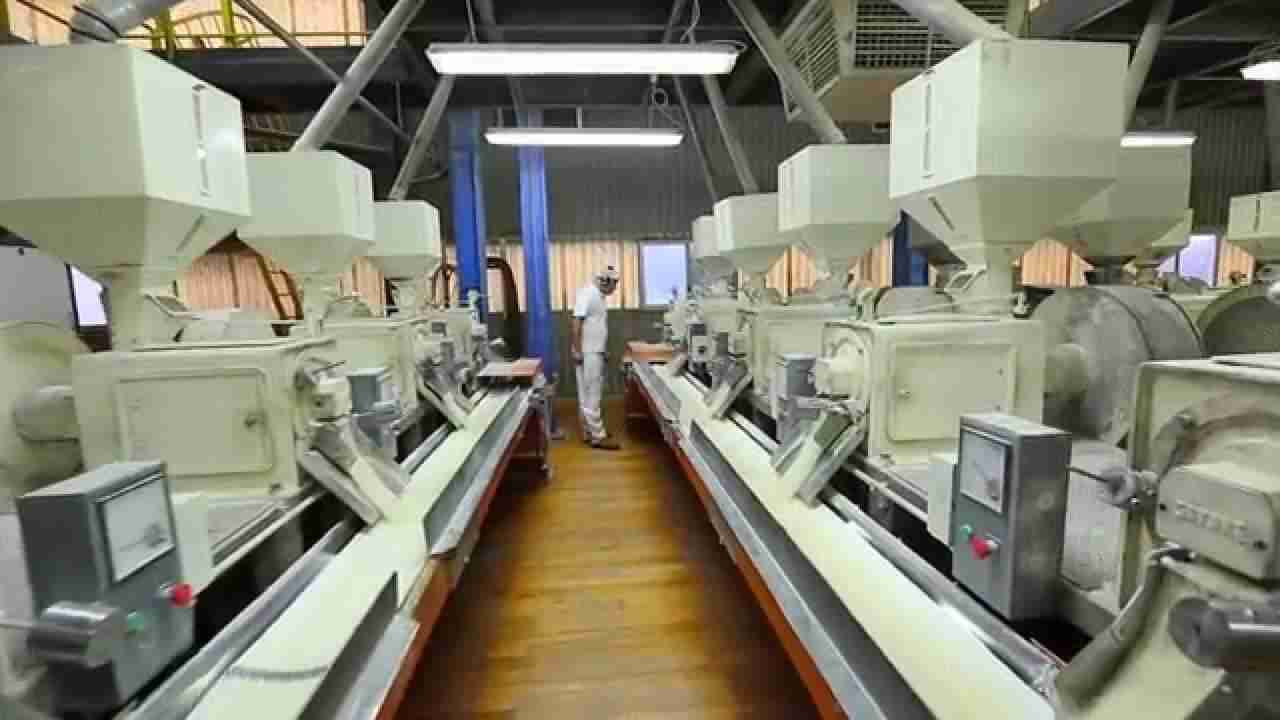
Exploring the Technology Behind Modern Rice Milling Units
Modern rice milling units have transformed the industry through the incorporation of advanced technology, enhancing both efficiency and product quality. These sophisticated machines rely on a combination of mechanical, electrical, and electronic systems, which streamline the entire milling process from paddy preparation to final product delivery. Key components that define these milling units include:
- Pre-cleaners: Remove impurities and defective grains to prepare paddy for milling.
- Huskers: Efficiently separate husk from brown rice without damaging the grains.
- Milling machines: Employ specific abrasion techniques to polish and remove bran layers.
- Separators: Sort different grades of milled rice based on size and weight.
- Packaging stations: Automate the filling and sealing of rice bags for distribution.
The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) has further elevated the capabilities of rice milling units. These systems can now monitor and control various parameters in real-time, ensuring optimal operational efficiency. By utilizing smart sensors, mill operators can track factors such as temperature, humidity, and grain quality, allowing for prompt adjustments to the milling process. A glimpse into the impact of technology can be seen in the following table:
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automation | Reduces labor costs and increases consistency. |
| Data Analytics | Enhances decision-making through real-time insights. |
| Energy-efficient motors | Minimizes energy consumption and lowers operational costs. |
Optimizing Efficiency: Best Practices for Rice Mill Operations
Efficient rice mill operations hinge on a multitude of factors that streamline processes while maintaining quality. Utilizing modern technology such as automated milling systems and integrated software can greatly enhance productivity. These systems not only decrease manual labor but also minimize human errors, leading to consistent results. Other effective approaches include regular maintenance schedules for machinery, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, training staff to understand best practices in both operation and safety can further reduce downtime and enhance mill efficiency.
Another critical aspect is the optimization of workflow within the milling unit. This can be achieved through careful layout design, facilitating smooth movement of rice from one stage to the next. For example, organizing equipment in a linear flow from raw paddy reception to milling and packaging can significantly cut down transit times. Implementing inventory management techniques also aids in minimizing stock wastage while ensuring availability. Here’s a simple table that outlines essential considerations for efficient rice milling:
| Consideration | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Equipment Maintenance | Schedule regular checks & repairs |
| Staff Training | Conduct workshops & simulations |
| Workflow Design | Implement a linear system layout |
| Inventory Management | Use automated tracking systems |
Sustainability in Rice Milling: Balancing Productivity with Environmental Responsibility
In the quest for maximizing output and efficiency, rice milling units often face the challenge of aligning productivity with ecological stewardship. Innovative practices are emerging within the industry, prioritizing methods that reduce waste and energy consumption. Various strategies can be integrated into milling operations, including:
- Utilizing solar energy systems to power mills, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Implementing water recycling processes to minimize consumption and prevent pollution.
- Adopting cleaner technology for husking and polishing, which decreases energy usage and emissions.
Moreover, community engagement and education play crucial roles in fostering sustainable practices. By collaborating with local farmers and communities, rice millers can not only optimize supply chains but also encourage a holistic approach to sustainability that includes:
- Promoting crop diversity to improve soil health.
- Implementing the circular economy principles—turning by-products, like rice husk, into valuable resources.
- Cultivating partnerships with environmental organizations to enhance preservation efforts.
In Summary
As we conclude our exploration of rice milling units, we have uncovered the intricate processes that transform raw grains into the staple foods we often take for granted. From the careful selection of paddy to the sophisticated technologies that ensure quality and efficiency, rice milling is a fascinating blend of tradition and innovation.
The stories behind these units reveal not only the technical mastery involved but also the cultural significance of rice in communities around the globe. As we move forward, it is essential to recognize the vital role that these milling units play in food security and economic development.
As we continue to “unlock the grain,” let us approach this age-old craft with a renewed appreciation for the labor and ingenuity that lie behind every grain of rice on our plates. In a world increasingly shaped by the challenges of sustainability and globalization, understanding the nuances of rice milling becomes ever more important. Here’s to the journey of grain, and the ceaseless efforts of those who ensure its availability for future generations.