Unlocking Potential: The Impact of Paddy Processing Units
In the heart of rural landscapes, where golden fields sway gently in the breeze, paddy rice stands as a vital staple, nourishing communities and economies alike. Yet, the journey from harvest to table is often overlooked, shrouded in the complexities of processing that hold the key to unlocking true value. Enter paddy processing units—unsung heroes in the agricultural narrative, equipped to transform raw grains into premium products that cater to both local and global markets. This article explores the multifaceted impact of these processing units, delving into how they not only enhance productivity and ensure food safety but also foster economic growth, empower farmers, and pave the way for sustainable practices. Join us as we uncover the profound implications of modern paddy processing and its role in shaping a resilient future for agriculture and communities worldwide.
Exploring the Role of Paddy Processing Units in Rural Development
In the heart of rural landscapes, paddy processing units emerge as catalysts for socio-economic transformation. They not only elevate local agricultural practices but also serve as pillars for sustainable rural development. By offering essential services such as milling, drying, and packaging, these units create a streamlined operation that benefits farmers and consumers alike. The establishment of these facilities often leads to a ripple effect throughout the community, fostering an environment where employment opportunities flourish, and local economies thrive. Farmers find themselves free from the burdens of manual processing, allowing them to focus more on cultivation, thereby enhancing productivity and yield.
Moreover, paddy processing units play a significant role in enhancing the marketability of rice products. By ensuring quality control and enhancing processing techniques, these facilities help producers achieve better pricing for their grains, directly boosting their incomes. The units also encourage entrepreneurial ventures in rural areas, as entrepreneurs are inspired to innovate new products and variations, leading to diversification in the local agri-food sector. Some impactful effects include:
- Improved food security by ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality rice
- Empowerment of women and marginalized groups through job creation and skills training
- Strengthened community ties through cooperatives and shared resources
| Benefits of Paddy Processing Units | Impact on Rural Development |
|---|---|
| Employment Generation | Increased local income and reduced migration |
| Quality Enhancement | Better market access for farmers |
| Community Development | Collaboration among farmers and stakeholders |
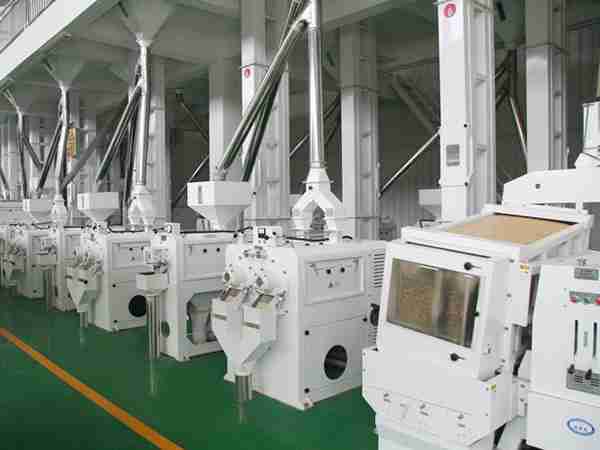
Innovative Technologies Transforming Paddy Processing Efficiency
In recent years, advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the efficiency of paddy processing units, leading to better yields and reduced waste. Modern machinery equipped with AI-driven analytics are capable of monitoring every stage of the processing line, ensuring superior quality control. Automated sorting systems use machine learning algorithms to separate grains based on size and weight, while automated husking and milling units increase throughput with minimal grain loss. This integration of technology not only optimizes production rates but also lowers labor costs significantly.
Additionally, the adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) technology has opened new avenues for real-time data collection and remote monitoring. Paddy processing units can now track moisture levels, grain quality, and equipment performance through connected sensors, providing actionable insights that help prevent downtime. These smart solutions have reduced post-harvest losses and enhanced traceability, allowing farmers and processors to maintain higher standards and meet market demands effectively. The result is a sustainable and resilient approach to paddy processing that underscores the importance of innovation in agriculture.
Enhancing Economic Viability Through Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable practices in paddy processing units offers a dual benefit: it not only enhances environmental stewardship but also significantly boosts economic viability. By adopting advanced technologies and eco-friendly methods, these units can reduce waste and optimize resource usage. For instance, utilizing biomass energy generated from rice husks to power machinery minimizes reliance on non-renewable energy sources. Furthermore, the introduction of water recycling systems can lead to major savings in operational costs, thereby increasing profit margins. Some other practices that can be embraced include:
- Organic pest control to maintain product integrity.
- Efficient logistics to decrease transportation costs.
- Community engagement programs to support local farmers.
Moreover, environmentally-conscious operations can attract a growing market of sustainability-minded consumers, creating brand loyalty and expanding market reach. Investment in state-of-the-art processing technologies not only enhances the quality of the final product but also increases yield and reduces processing time. To illustrate the remarkable advantages of adopting these practices, the table below details potential cost savings and additional revenue streams for paddy processing units:
| Practice | Cost Savings (Annual) | Additional Revenue Streams |
|---|---|---|
| Biomass Energy Use | $10,000 | Sale of excess energy |
| Water Recycling | $5,000 | Reduced utility costs |
| Organic Certification | N/A | Premium pricing for organic products |
These enhancements not only position paddy processing units for financial success but also contribute to a sustainable future by reducing their environmental footprint. The confluence of economic growth and ecological responsibility empowers these centers to thrive in an ever-evolving industry landscape.
Policy Recommendations for Strengthening Paddy Processing Opportunities
To leverage the full potential of paddy processing units, it is essential to implement well-structured policies that foster growth and innovation. One of the key recommendations is to establish subsidies for equipment and technology upgrades, enabling small and medium enterprises to modernize their facilities. Access to financial support can encourage investment in efficient machinery, thus increasing productivity and improving product quality. Additionally, governments should consider creating cooperative models that allow farmers to pool resources and share the benefits of processing facilities. This collaborative approach can enhance economies of scale, making it feasible for smaller producers to participate in the market more competitively.
Training and capacity-building programs are pivotal in increasing the skill set of workers in the paddy processing sector. By developing educational initiatives focused on best practices and new technologies, stakeholders can better adapt to market demands and improve overall processing efficiency. Furthermore, it’s crucial to establish value chain partnerships that connect paddy processors with stakeholders such as suppliers, distributors, and retailers. These partnerships can optimize logistics, reduce waste, and lead to the development of new market opportunities, ultimately contributing to the sustainability and growth of the paddy processing industry.
Insights and Conclusions
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of paddy processing units and their transformative impact, it becomes clear that these humble facilities do far more than merely refine rice. They serve as vital nodes in the agricultural ecosystem, enhancing productivity, ensuring food security, and fostering economic resilience in rural communities. The journey from paddy to plate is not just a testament to technological advancement, but a celebration of the potential that lies untapped within the grains of rice. By investing in and supporting such processing units, we unlock a realm of possibilities—not just for farmers and economies, but for societies striving toward sustainability and growth. As the world navigates an increasingly complex landscape, the lessons learned from these units remind us that the roots of innovation often lie in the heart of our most traditional practices. The future of agriculture, it seems, is not just about what we grow, but how we choose to process and appreciate the fruits of our labor.