In the hushed embrace of early dawn, as the world stirs from slumber, a transformative process unfolds—one that has been refined over centuries yet remains steeped in tradition. “Grain to Grind: The Art and Science of Cereal Milling” invites you to explore this intricate journey, where nature’s bounty is meticulously processed into the flour that nourishes our daily lives. Bridging the past and the present, cereal milling blends artistry with engineering, drawing on both the natural properties of grains and the precision of modern technology. From the golden fields where grains are harvested to the rhythmic pulse of millstones working in harmony, this article delves into the myriad techniques that define milling and celebrates the alchemy involved in turning simple kernels into staple ingredients. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind this essential craft that has fed generations, shaped cultures, and continues to evolve in an ever-changing world.
Understanding Grain Composition and Its Impact on Milling Techniques
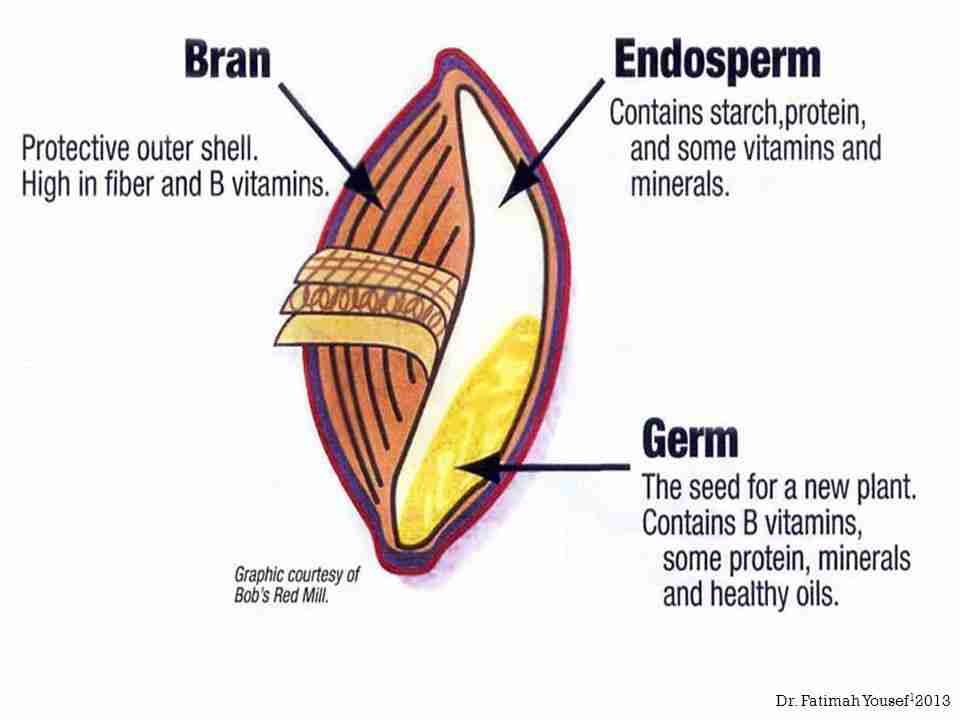
Grain composition plays a significant role in determining the efficiency and outcome of milling operations. The chemical and physical properties of grains, such as moisture content, protein levels, and hardness, directly influence the choice of milling techniques. For instance, high-protein grains like durum wheat necessitate a different milling approach compared to softer grains such as white wheat. Each grain type presents its unique challenges and requires tailored processing methods to maximize yield and quality.
Moreover, understanding the functional characteristics of grains can lead to enhanced product development. Key factors like particle size distribution, bran and germ content, and endosperm quality must be meticulously examined. Here are some pivotal components to consider in milling:
- Moisture Content: Impacts shelf life and milling efficiency.
- Grain Hardness: Affects the energy required for grinding.
- Endosperm Quality: Determines flour’s baking performance.
- Bran and Germ Composition: Influences nutritional and sensory properties.
| Grain Type | Protein (%) | Hardness | Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durum Wheat | 12-16 | Very Hard | 8-12 |
| Hard Red Spring | 13-16 | Hard | 10-14 |
| Soft White Wheat | 8-12 | Soft | 10-13 |
Mastering Milling Machinery for Optimal Grain Processing
Understanding the intricate dynamics of milling machinery is crucial for achieving the highest efficiency in grain processing. The art of milling not only involves the physical mechanisms of grinding and sifting but also requires a nuanced appreciation for the types of machinery employed. From roller mills to hammer mills and stone grinders, each type brings its unique attributes to the milling process. Effective management of these machines can enhance the quality of the final product, leading to flour that is both flavorful and nutritious. This mastery involves regular maintenance, calibration, and the ability to adapt settings based on the moisture content and type of grain being processed.
Moreover, the significance of grain selection and machine configuration cannot be overstated. Implementing the right milling method ensures that the starches, proteins, and gluten levels are optimized, providing the desired texture and taste profile for the flour. Key aspects to consider include:
- Grain Type: Hard vs. soft; each requires different milling techniques.
- Particle Size: Effects on baking quality and texture.
- Temperature Control: Ensures the integrity of the grain’s nutrients.
To illustrate the relationship between grain types and their suitable milling methods, consider the following table:
| Grain Type | Milling Method | End Product Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Roller Mill | High gluten strength, fine texture |
| Rye | Stone Grinder | Coarse, earthy flavor |
| Corn | Hammer Mill | Gritty texture, ideal for tortillas |
By mastering these aspects of milling machinery, professionals can ensure that their grain processing aligns with industry standards while delighting consumers with high-quality products.
Innovative Approaches to Quality Control in Cereal Production
In the evolving landscape of cereal production, innovative quality control measures are essential to ensure product excellence and consumer satisfaction. Advances in technology have paved the way for a more integrated approach to monitoring grain integrity, with tools that enable producers to maintain above-standard safety and quality protocols. Key strategies include:
- Automation: Implementing automated systems for grain testing helps expedite the identification of contaminants and deviations in quality, allowing for quicker decision-making.
- AI-Driven Analytics: Machine learning algorithms analyze data from various production stages to predict potential quality issues before they arise.
- Tiered Satisfaction Metrics: Developing multi-layered satisfaction metrics ensures that every level of production—from processing to packaging—meets rigorous standards.
Additionally, collaboration among industry stakeholders fosters a holistic approach to quality assurance. Regular workshops and knowledge-sharing sessions promote innovative solutions drawn from collective experiences. Establishing a transparent reporting framework ensures data flow between producers and consumers is seamless. An exemplary collaborative model is showcased in the following table:
| Stakeholder | Role | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Farmers | Raw Material Providers | Quality Grain Sourcing |
| Mill Operators | Production Executives | Process Optimization |
| Quality Assurance Teams | Quality Overseers | Standards Compliance |
| Retailers | Market Distributors | Consumer Feedback Integration |
This collaborative environment not only enhances production quality but also builds consumer trust, solidifying the importance of innovative quality control in the cereal milling industry.
Sustainability in Milling: Practices for a Greener Future
Embracing sustainability in the milling industry is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for the preservation of our environment. Many milling operations are focusing on energy efficiency and waste reduction to minimize their ecological footprint. By investing in modern technology, mills are able to utilize resources more effectively, achieving maximum output while using minimal input. This includes the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, which significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, many mills are implementing water conservation practices, such as recycling and treating wastewater to ensure that this vital resource is used judiciously.
Incorporating sustainable practices into the milling process also extends to sourcing raw materials responsibly. This involves collaborating with local farmers who employ sustainable agricultural techniques. By reducing transportation emissions and supporting local economies, mills can contribute to a more sustainable food system. Furthermore, the promotion of whole grain products encourages healthier eating habits and utilizes the entire grain, thereby minimizing waste. The table below highlights some sustainable practices that are becoming standard in the milling industry:
| Sustainable Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Optimization | Use of energy-efficient machinery and renewable energy sources to lower carbon footprint. |
| Water Recycling | Implementing strategies to recycle and treat wastewater for reuse in milling processes. |
| Local Sourcing | Partnering with local farmers adopting sustainable agriculture to reduce transportation emissions. |
| Whole Grain Utilization | Prioritizing whole grains to minimize waste and promote a healthier product range. |
The Way Forward
As we reach the end of our exploration into the intricate world of cereal milling, it becomes evident that this process is more than just a means to an end; it is a delicate balance of art and science. From the careful selection of grains to the precision of modern milling techniques, every step contributes to the final product that nourishes our bodies and shapes our culinary experiences. The age-old traditions blended with innovative technologies remind us of the rich tapestry that food creation weaves around our lives.
In understanding the journey from grain to grind, we gain insight not only into the mechanics of milling but also into the cultural significance of the grains themselves. We invite you to appreciate the story behind each flour bag or cereal box, recognizing the craftsmanship and dedication that have evolved over centuries. As we continue to savor the benefits of this intricate process, let us honor the grains that play a pivotal role in our diets and celebrate the skilled hands that bring them to our tables.
So, next time you sprinkle flour for a homemade loaf or pour a bowl of cereal, pause for a moment and reflect on the artistry and science that have brought these simple yet profound staples into your life. The journey from grain to grind is not just about nourishment; it’s a testament to our connection with food and the enduring legacy of those who labor to keep our traditions alive.