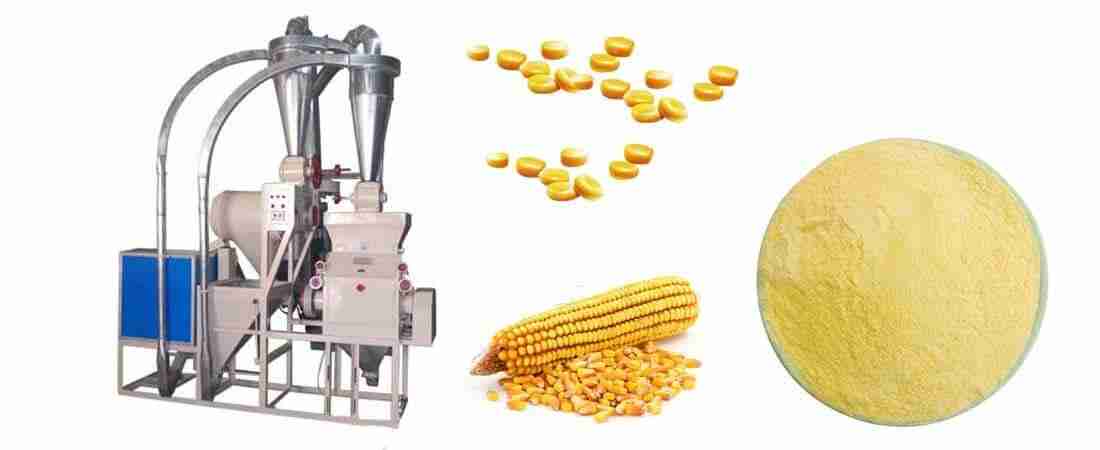
Transforming Grains: The Art and Science of Maize Milling
In the heart of every vibrant culinary culture lies a humble truth: the transformation of grains is both an ancient art and a modern science. Among these grains, maize stands out, rich in history and diversity, offering a canvas for innovation. From the bustling markets of Central America to the artisanal mills scattered across the rural landscapes, the craft of maize milling has evolved as a crucial intersection of tradition and technology. As we delve into the intricate world of maize milling, we unveil the nuanced processes that convert raw kernels into staple ingredients, each step guided by a blend of age-old techniques and cutting-edge practices. Join us on a journey through the mills and kitchens where the simple act of transforming maize ignites flavors, fuels communities, and nurtures cultures, illuminating the profound relationship between grain and the gastronomic experiences that depend upon it.
Exploring the Historical Roots of Maize Milling Techniques
The journey of maize milling techniques is steeped in rich cultural heritage, echoing the practices of various civilizations that have crafted intricate methods of processing this vital crop. As maize migrated from its origins in Mesoamerica, it underwent a transformation, influenced by diverse agricultural and culinary traditions. Early civilizations, such as the Aztecs and Maya, utilized rudimentary tools like mortars and pestles for grinding maize into flour, a vital component of their diets. Over centuries, these techniques evolved into more sophisticated milling methods, with innovations like the stone mill, which allowed for finer textures and an increased variety of maize-based products. The incorporation of water mills during the medieval period marked a significant turning point, showcasing an intersection of ingenuity and practicality in food production.
The global spread of maize milling techniques provided fertile ground for cross-cultural exchanges that enriched culinary practices. Various methods developed in different regions, emphasizing regional preferences and available resources. For instance, in Africa, traditional methods remain prevalent, where communities often use hand-operated stone mills that preserve local flavors and texture. In contrast, the industrial revolution introduced mechanized milling, drastically changing the landscape by increasing efficiency and accessibility. Here’s a brief overview of key maize milling techniques from around the world:
| Region | Traditional Technique | Modern Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | Stone grinding | Nixtamalization with modern mills |
| Africa | Hand-operated stone mills | Electric hammer mills |
| United States | Horse-drawn grist mills | Large-scale industrial milling |
Understanding the Modern Machinery and Technologies in Grain Processing
In the world of grain processing, the evolution of machinery and technology is paramount to enhancing efficiency and product quality. Today’s milling operations incorporate state-of-the-art machines, ensuring precise grain analysis and optimized processing techniques. Among the innovations seen in this industry are:
- High-Performance Rollers: Used for crushing and grinding grain, these systems ensure consistent particle size and flour quality.
- Advanced Sifting Systems: Automated sifters help in the separation of different flour grades, allowing for specialized product offerings.
- Digital Control Panels: These offer real-time monitoring and adjustment of milling parameters, enhancing operational precision.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Modern machinery is designed to minimize energy usage, thus promoting sustainable milling practices.
Additionally, integration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized grain processing. These innovations allow for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maximizing throughput. The impact of this technological advancement can be illustrated as follows:
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| AI in Quality Control | Real-time detection of defects leads to superior grain quality. |
| IoT Sensors | Continuous monitoring provides insights that drive decision-making. |
| Cloud Computing | Facilitates data storage and accessibility for operational analysis. |
Nutritional Enhancements: Transforming Maize into Healthier Food Options
In recent years, the quest for healthier food options has led to innovative approaches in enhancing the nutritional profile of maize. By focusing on biofortification, researchers and food technologists have begun to enrich maize with essential vitamins and minerals. This process aims to increase the content of nutrients such as iron, zinc, and folate within the grain itself, turning it into a powerhouse of nutrition. The incorporation of various leguminous plants in intercropping strategies is another effective method, as it not only enriches the soil with nitrogen but also enhances the amino acid profile of maize, making it an even more balanced food source.
Furthermore, the milling process has undergone significant transformations to maximize nutrition retention. Advanced milling technology allows for the production of whole grain flour, which preserves the bran and germ, vital components that contribute to dietary fiber, antioxidants, and essential fatty acids. This revolution in milling practices promotes not just the consumption of maize flour but also encourages a variety of healthy culinary applications. Here’s a snapshot of some common nutritional enhancements:
| Nutritional Enhancement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Iron Fortification | Improves hemoglobin levels, reducing anemia risks. |
| Zinc Enrichment | Boosts immune function and aids in wound healing. |
| Vitamin A Addition | Enhances vision and supports immune response. |
Such enhancements not only transform maize into a more nutritious option but also align with global efforts to combat malnutrition. Emphasizing the incorporation of these fortified products in daily diets serves not only to elevate individual health standards but also to promote sustainable agricultural practices that benefit entire communities.
Sustainability in Maize Milling: Practices for a Greener Future
As the world increasingly embraces sustainable practices, the maize milling industry has a unique opportunity to contribute significantly to environmental stewardship. By adopting innovative techniques and technologies, milling operations can minimize their ecological footprint. Key strategies include:
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing energy-efficient machinery and integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can dramatically reduce carbon emissions.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water recycling systems and rainwater harvesting methods helps conserve this precious resource, especially in areas prone to drought.
- Waste Reduction: Repurposing milling byproducts, like husks and bran, for animal feed or bioenergy can significantly reduce waste and enhance overall sustainability.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Transitioning to biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials further minimizes environmental impact.
Additionally, collaboration across the supply chain is vital to fostering a culture of sustainability. This can be achieved by:
- Educating Farmers: Encouraging local maize farmers to adopt sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation and organic farming, enhances soil health and reduces dependency on chemical fertilizers.
- Community Engagement: Partnering with local communities to promote awareness and conservation efforts can drive collective action towards sustainability goals.
- Certifications and Standards: Obtaining eco-certifications assures consumers of a commitment to environmental responsibility and can open doors to new market opportunities.
| Sustainable Practice | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy costs, reduced emissions |
| Water Conservation | Preserved water resources, lower utility bills |
| Waste Reduction | Minimized waste, additional revenue streams |
| Eco-Friendly Packaging | Reduced plastic use, enhanced brand image |
Wrapping Up
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of “Transforming Grains: The Art and Science of Maize Milling,” it becomes clear that this process is far more than mere machinery and labor—it is a harmonious blend of history, culture, and innovation. The humble maize kernel, deeply rooted in traditions across the globe, plays a pivotal role in feeding millions and shaping culinary landscapes.
Every grind tells a story, every flour a legacy, echoing the ingenious techniques of ancestors while embracing modern advancements. From artisanal mills in remote villages to sprawling industrial facilities, the journey of maize from field to table is a testament to human ingenuity and resilience.
As we savor the products of maize milling, let us appreciate the intricate dance of science and art that transforms simple grains into versatile staples. In this age of rapid technological progress, may we remember to honor the roots of this essential grain—the essence of which fuels not only our bodies but also our communities and cultures. The next time you enjoy a dish featuring maize, take a moment to reflect on the profound journey it has undertaken, celebrating both the past and the future of this remarkable grain.