Transforming Grain: Inside the World of Paddy Processing Plants
In the heart of thriving rice-producing regions, where vast emerald fields stretch to the horizon, the journey from raw grain to pantry staple begins. Paddy processing plants serve as the crucial nexus in this transformation, converting harvested paddy into the polished white rice that graces tables around the world. Yet, behind the rhythmic hum of machinery and the bustling workforce lies a complex interplay of tradition, technology, and sustainability. This article invites you to explore the intricate processes that define paddy processing, shedding light on the innovations driving efficiency, the challenges faced by industry players, and the far-reaching impact on global food security. Join us as we delve into this essential yet often overlooked segment of the agricultural sector, where every grain tells a story of transformation.
Exploring the Journey from Field to Facility: Understanding Paddy Processing Dynamics
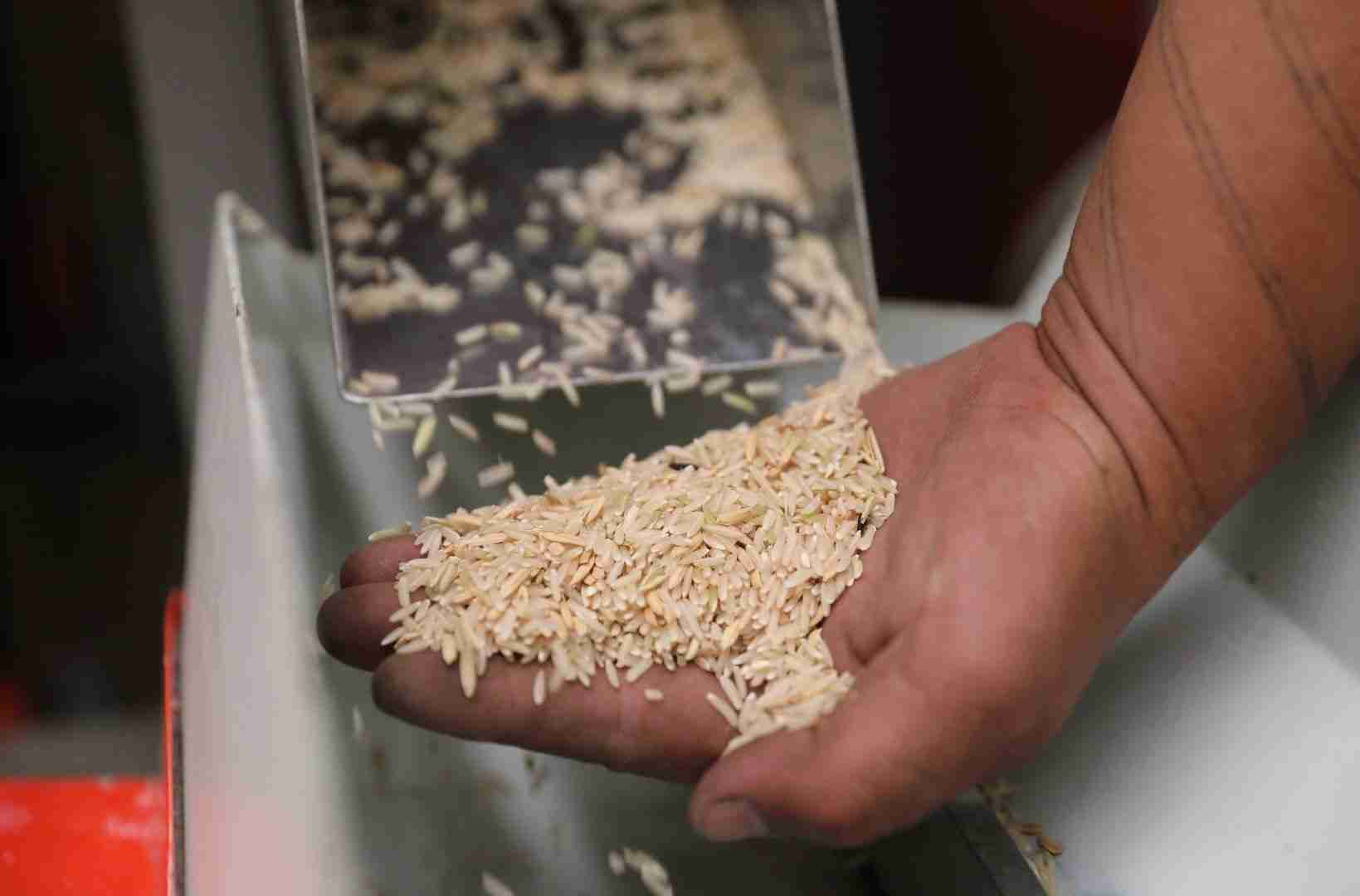
The journey of paddy from the lush green fields to the bustling processing facilities is a remarkable transformation marked by a blend of tradition and modern technology. Farmers work diligently during the harvest, gathering the golden grains that will soon undergo a meticulous journey. Once collected, the paddy is transported to processing plants, where it undergoes several crucial steps to unlock its potential as a staple food source. The processing involves a series of phases, including soaking, steaming, and drying, all aimed at enhancing the quality and shelf-life of the rice. By employing state-of-the-art machinery, facilities not only improve efficiency but also ensure that the nutritional value of the grains is preserved during processing.
Within the processing facility, various techniques are utilized to maximize output and maintain quality. The steps can be summarized as follows:
- Cleaning: Removing impurities and foreign materials from the harvested paddy.
- Hulling: The outer husk is removed to reveal the brown rice beneath.
- Milling: Further processing transforms brown rice into white rice, enhancing its appeal.
- Polishing: A final step that gives rice its bright and appealing appearance.
These operations not only serve to prepare the grain for market but also embody a deeper connection to cultural practices surrounding rice consumption. Understanding the dynamics of paddy processing sheds light on the intricate balance between agricultural methods and technological advancement. Below is a simple overview showcasing the stages involved in the transformation of paddy to rice:
| Processing Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collecting ripe paddy grains from the fields. |
| Transportation | Moving harvested paddy to processing facilities. |
| Cleansing | Eliminating dirt and other unwanted materials. |
| Milling | Transforming brown rice into polished white rice. |
Essential Technologies Driving Efficiency in Paddy Processing Plants
Paddy processing plants have become pivotal in enhancing the efficiency of rice production through the integration of advanced technologies. The adoption of automated milling systems reduces manual labor requirement and speeds up the processing time significantly. These systems utilize precision equipment that ensures the optimal extraction of rice from paddy, minimizing waste and maximizing yield. Furthermore, optical sorters employ cutting-edge image recognition technology to identify and separate defective grains, thus elevating the overall quality of the final product. This level of automation not only enhances productivity but also assures consistent quality throughout the processing stages.
Another technology driving efficiency is smart grading systems that leverage data analytics to monitor and optimize various facets of operations. This system collects real-time data, allowing plant managers to make informed decisions based on production trends and quality assessments. Additionally, energy-efficient machinery reduces operational costs while minimizing the carbon footprint of processing plants. Utilizing equipment that operates with lower energy consumption can significantly impact profitability. Together, these technologies form a cohesive framework that not only transforms raw paddy into premium rice products but also establishes a benchmark for sustainability in the agricultural sector.
Quality Control Measures: Ensuring a Premium Product from Grain to Rice
In the intricate world of paddy processing, ensuring the highest quality product requires a meticulous approach at every stage. Quality control measures begin right at the reception of raw grain, where samples are taken to analyze moisture content, impurities, and overall grain health. Each batch undergoes rigorous testing against established quality parameters, which include:
- Moisture Content: Monitored to prevent spoilage and ensure optimal cooking qualities.
- Impurity Levels: Regular checks to eliminate foreign materials and maintain purity.
- Kernel Integrity: Assessing the physical condition of the grains to determine their suitability for milling.
As processing unfolds, additional quality checkpoints are integrated throughout the milling process. Advanced technology and skilled professionals work coherently to enhance quality through stages such as husking, whitening, and grading. Each stage implements automated systems and human oversight to adhere to strict quality standards. Essential aspects of control in this phase include:
| Process Step | Quality Check |
|---|---|
| Husking | Assessment of hull removal efficiency |
| Whitening | Monitoring of rice color and texture |
| Grading | Classification of rice by size and quality |
The end goal is to deliver a premium product that not only meets but exceeds consumer expectations, making quality control an indispensable part of the wheat to rice transformation journey.
Sustainable Practices in Paddy Processing: Balancing Productivity and Environmental Responsibility
In the heart of paddy processing plants, the challenge of maximizing output while minimizing environmental impact has never been more critical. Sustainable practices have emerged as the backbone of innovative operations, significantly influencing efficiency and resource management. Key initiatives include:
- Waste Recycling: Utilizing by-products like rice husks and bran as biofuels or soil conditioners helps to reduce landfill waste and enhances nutrient cycling.
- Water Management: Implementing advanced irrigation systems and water recycling methods minimizes freshwater consumption and maintains local ecosystems.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing solar panels and energy-efficient machinery to reduce carbon footprints, transforming potential emissions into opportunities for sustainable energy use.
Moreover, the focus on organic and chemical-free processing methods aligns the industry with consumer trends toward healthier food choices. To track the impacts of these sustainable measures, many facilities utilize performance metrics such as:
| Practice | Impact |
|---|---|
| Water Recycling | Reduces water usage by 30% |
| Energy-Efficient Equipment | Lowers energy costs by 25% |
| Waste Biomass Utilization | Generates 70% of plant energy needs |
These metrics not only provide insight into operational success but also create transparency, allowing stakeholders and consumers to understand the balance between productivity and environmental stewardship in the paddy processing sector.
Key Takeaways
As we conclude our exploration of the intricate journey within paddy processing plants, it’s clear that this seemingly straightforward agricultural endeavor is anything but simple. From the moment paddy arrives in bulk to the meticulous steps of husking, milling, and polishing, each phase is a dance of technology and tradition, harmonizing to meet the demands of a global market.
The processes that transform grain not only shape the rice we ultimately consume but also impact the livelihoods of countless farmers, workers, and communities that depend on this critical staple. Understanding the significance of these plants illuminates the connection between our plates and the dedicated individuals behind the scenes.
As we reflect on the vital role of paddy processing in the food supply chain, we are reminded that each grain has a story—a story of hard work, innovation, and sustainability. The next time you sit down to enjoy a simple bowl of rice, may you appreciate the intricate network of processes that brought it to your table, and consider the ongoing evolution of paddy processing as it adapts to meet the challenges of the future. In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and efficiency, the potential for transformation within this realm is as vast as the fields that yield the grain.