Crunching the Numbers: A Deep Dive into Cereal Processing
In a world where breakfast often dictates the direction of our day, the humble bowl of cereal emerges as a remarkable staple—one that expertly blends convenience, nutrition, and nostalgia. But have you ever paused to contemplate the journey from field to table? Behind every crisp flake and puffed grain lies a complex web of processing methods and industry practices that transform raw ingredients into the cereals we know and love. In “Crunching the Numbers: A Deep Dive into Cereal Processing,” we will explore the intricate processes that underpin this billion-dollar industry. Through insightful analysis and detailed examination of production techniques, ingredient selection, and sustainability efforts, we aim to unravel the fascinating science and art of cereal processing. Join us as we dissect the numbers and take a closer look at the mechanisms that turn oats, corn, and wheat into breakfast powerhouses.
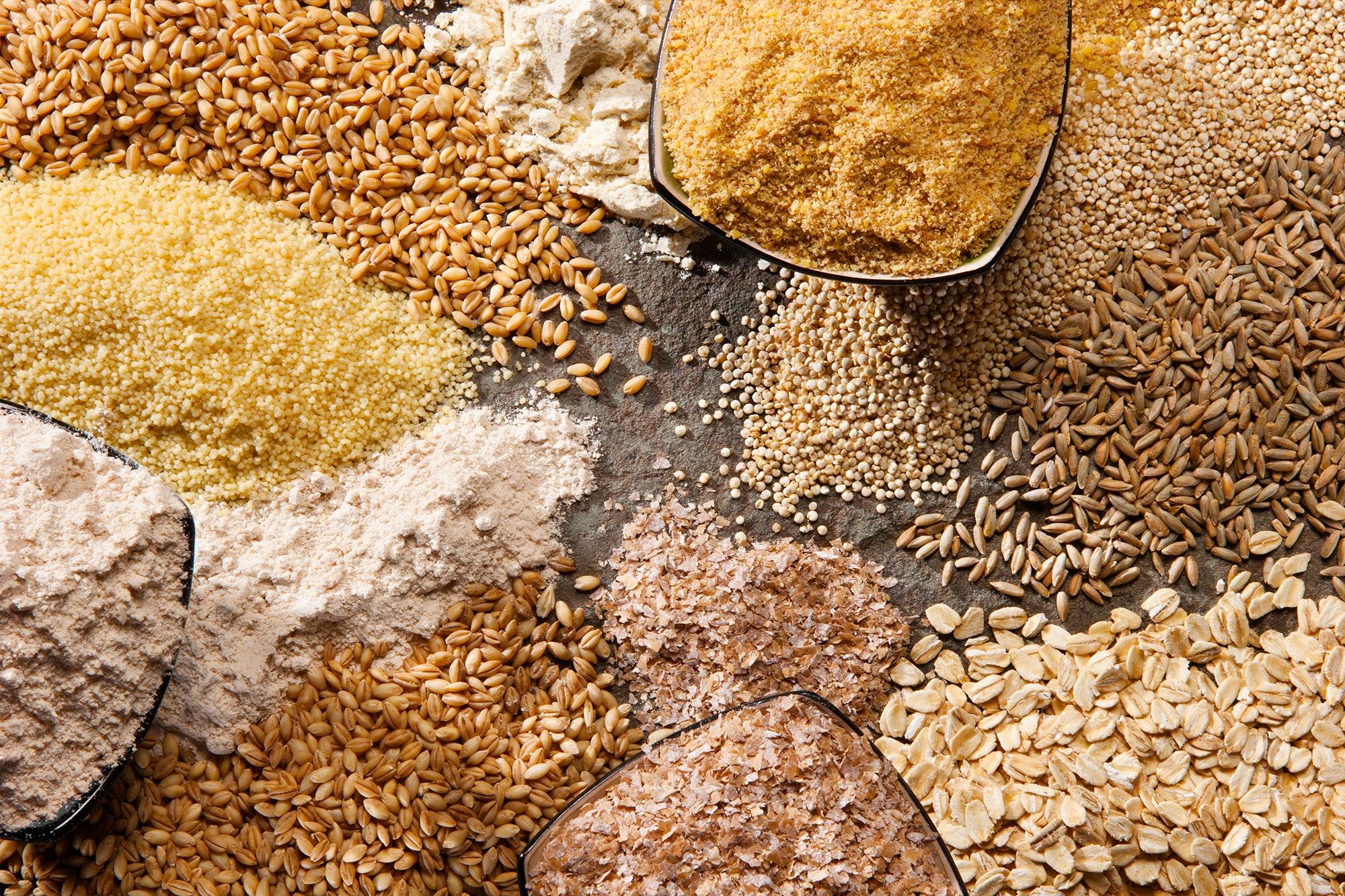
Exploring the Lifecycle of Cereal Grain from Farm to Bowl
Cereal grains embark on a remarkable journey from the fields to our breakfast bowls, undergoing several transformative stages along the way. It all begins on the farm, where farmers nurture cereal crops such as wheat, barley, and rice, carefully monitoring factors like soil health, water availability, and pest management. Once harvested, the grains enter the post-harvest phase, where they are cleaned, dried, and stored to prevent spoilage. At this stage, the grain’s quality is paramount, laying the groundwork for the processing that follows. Key activities during this phase include:
- Harvesting: Timing is crucial, as moisture content can significantly influence grain quality.
- Cleaning: Removing impurities like weeds and stones ensures only the best grains are processed.
- Drying: Reducing moisture content prevents mold and preserves freshness.
After storage, the processing phase transforms the raw grains into the familiar products we find on grocery shelves. This stage can include milling, where whole grains are ground into flour, and further processing to create breakfast cereals and snacks. During milling, the grain is broken down into various components, such as bran, germ, and endosperm, each offering different nutritional benefits. Subsequent processes might involve:
| Processing Stage | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Milling | Producing flour or granulated grains for various uses |
| Toasting | Enhancing flavor and texture in breakfast cereals |
| Fortification | Adding vitamins and minerals to improve nutrition |
In addition to these processes, packaging plays a critical role in preserving the cereal’s quality and extending shelf life, ensuring that each bite remains as fresh and nutritious as intended. By tracing the journey of cereal grains, we can appreciate the intricate systems and passionate individuals involved in bringing wholesome breakfast options to our tables.
Innovative Processing Techniques Enhancing Nutritional Value
In the realm of cereal processing, several innovative techniques have emerged that not only streamline production but also significantly enhance the nutritional profile of our favorite breakfast staples. One such method is extrusion cooking, which involves forcing a mixture of grains, water, and other ingredients through a die under high temperature and pressure. This process not only improves the texture and digestibility of cereals but also facilitates the infusion of essential vitamins and minerals, ensuring that consumers receive optimized nourishment with every bite. Another notable technique is fermentation, which harnesses the power of beneficial microorganisms. By fermenting grains, producers unlock a wealth of micronutrients, making them more bioavailable and boosting overall health benefits.
Equally transformative are advances in hydrothermal treatment, which utilize steam and heat to enhance protein digestibility and eliminate undesirable antinutritional factors such as phytic acid. Moreover, cutting-edge approaches such as microwave processing allow for reduced cooking times while preserving vitamins that are often lost during conventional methods. These techniques, along with the adoption of sprouting that increases nutrient activation and enhances flavor profiles, illustrate a shift towards holistic food production. The integration of these strategies not only targets improved health outcomes but also caters to the growing consumer demand for functional foods that deliver more than just basic sustenance.
| Processing Technique | Nutritional Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extrusion Cooking | Enhances digestibility and boosts nutrient absorption |
| Fermentation | Increases bioavailability of micronutrients |
| Hydrothermal Treatment | Improves protein digestibility and reduces antinutritional factors |
| Microwave Processing | Reduces cooking time while preserving vitamins |
| Sprouting | Activates nutrients and enhances flavors |
The Role of Quality Control in Maintaining Product Integrity
In the realm of cereal processing, quality control serves as the indispensable backbone of product integrity. It encompasses a series of systematic evaluations and tests designed to identify potential flaws in both ingredients and the final product. Each batch of grains is rigorously assessed for factors such as moisture content, nutritional value, and flavor profile. By employing a combination of sensory analysis and precision measurements, manufacturers can ensure that only the best inputs are utilized, setting the stage for a superior breakfast experience. Adhering to industry standards not only augments the product’s consistency but also reinforces consumer trust and brand loyalty.
The implementation of quality control measures includes various checkpoints throughout the production line, ensuring that every aspect contributes to the final outcome. Among the most pivotal methods employed are:
- Raw Material Inspection: Assessing grains and additives upon arrival.
- In-Process Testing: Monitoring parameters during processing to identify abnormalities.
- Final Product Evaluation: Conducting taste tests and lab analysis before packaging.
| Cereal Type | Moisture Content (%) | Protein Level (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oat Flakes | 5.5 | 13.2 |
| Corn Puffs | 3.8 | 8.5 |
| Wheat Bites | 6.0 | 12.0 |
Through these meticulous processes, quality control not only plays a critical role in obtaining regulatory compliance but also serves as an ongoing commitment to excellence. By fostering a culture of vigilance and continuous improvement, cereal processors can enhance their operational workflows while ensuring that every bowl served is not only delicious but also safe and nutritionally balanced. This methodical dedication to quality is what ultimately strengthens the foundation of product integrity in the cereal industry.
Sustainable Practices in Cereal Processing for a Greener Future
In the quest for a more sustainable future, the cereal processing industry is embracing innovative strategies that reduce environmental impact while maintaining product quality. Reducing energy consumption is a primary focus; companies are investing in more efficient machinery and alternative energy sources such as solar and wind. Additionally, optimizing operational logistics not only minimizes waste but also lowers carbon footprints. Another important aspect is water conservation, where advanced recycling systems are implemented to use treated water for various processing stages, significantly reducing freshwater dependency.
Moreover, the integration of biodegradable packaging materials is gaining momentum, reflecting a shift towards ecological responsibility. Rather than relying on traditional plastics, manufacturers are exploring options made from plant-based materials or other sustainable resources. In addition, the industry is re-evaluating supply chain practices to prioritize local sourcing, which supports local economies while cutting down on transportation emissions. This multidimensional approach ultimately aims to create a circular economy, enabling the reuse of by-products and fostering better environmental stewardship throughout cereal processing.
| Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces operational costs and carbon emissions |
| Water Recycling | Conserves freshwater resources |
| Biodegradable Packaging | Minimizes plastic pollution |
| Local Sourcing | Supports local economies and reduces transport emissions |
Closing Remarks
the world of cereal processing is a fascinating blend of innovation, science, and tradition. As we’ve explored, each step in the production chain—from cultivation to packaging—plays a pivotal role in shaping the final product that fills our breakfast bowls. The meticulous attention to detail and adherence to food safety standards ensure not only quality but also the nutritional value that fuels our day.
As consumers, understanding the intricacies behind the crunchy morsels we enjoy can deepen our appreciation for the cereal industry. Whether you’re a fan of sweetened flakes or fiber-rich granola, each bite is the result of a complex interplay of methods and technologies designed to enhance taste and texture while delivering essential nutrients.
So the next time you pour your favorite cereal, take a moment to think about the journey of those grains. Behind every box lies a rich narrative of agricultural expertise, cutting-edge processing techniques, and a commitment to bringing wholesome breakfasts to tables around the world. As the cereal industry continues to evolve, one thing remains certain: the crunch will always tell a story.