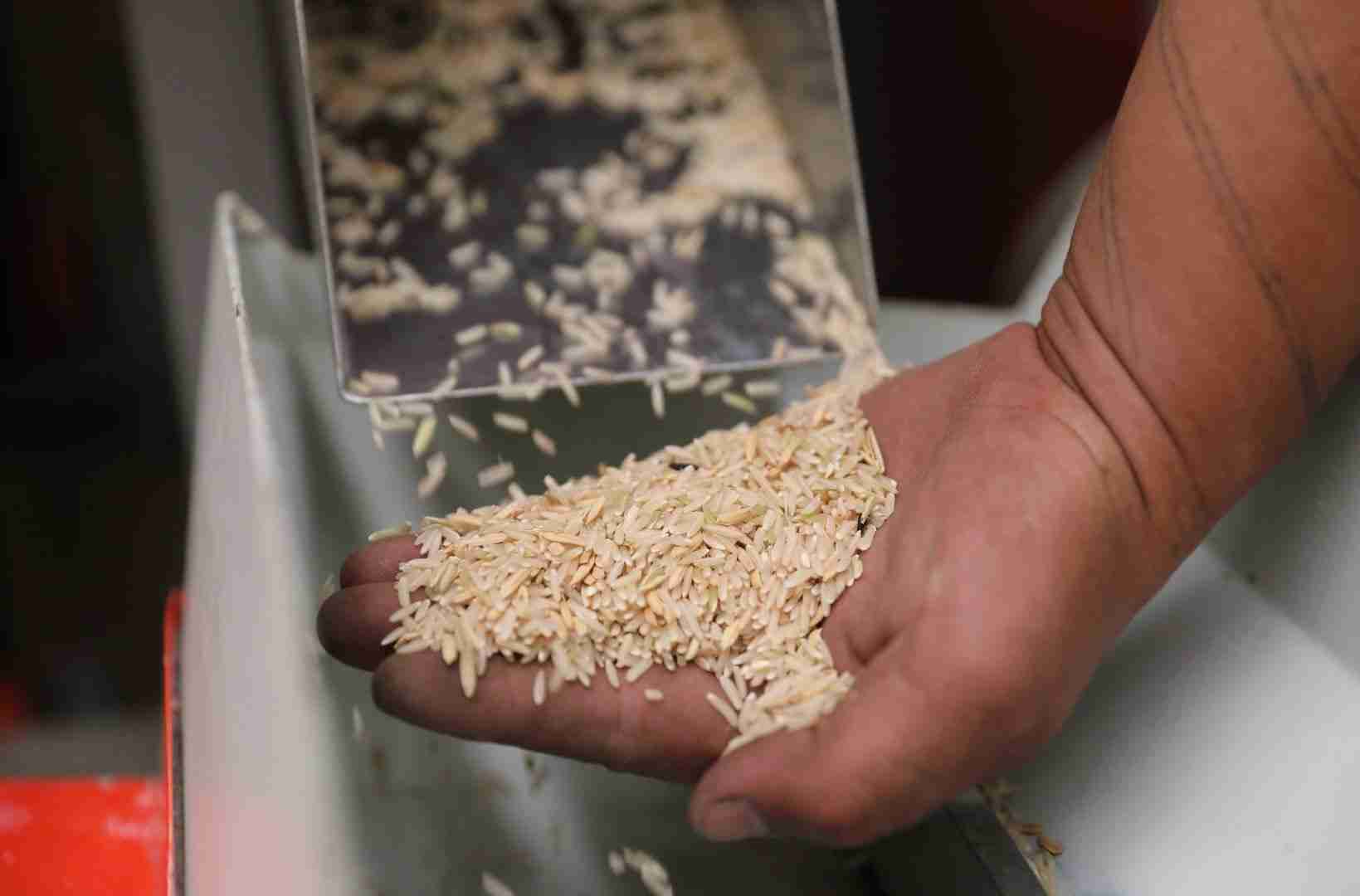
In the heart of agriculture lies a humble yet transformative staple: grains. Among them, rice stands out as a global essential, nourishing billions and shaping cultures. Yet, before it graces our plates, rice undergoes a remarkable metamorphosis, the intricacies of which unfold within the bustling confines of paddy processing plants. These facilities serve as the unsung heroes behind the scenes, orchestrating a delicate balance of science and tradition. From the initial husking to the final polishing, the journey of paddy into polished grains is a testament to human ingenuity and an intricate understanding of nature’s gifts. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted world of paddy processing plants, exploring the technologies, methods, and individuals that together transform a simple crop into a culinary cornerstone, all while navigating the challenges and innovations that shape this vital industry. Join us as we uncover the processes that turn paddy into a staple, illuminating the path from field to fork.
Exploring the Journey from Field to Mill: Understanding Paddy Processing
From the moment paddy is harvested, it embarks on a transformative journey that involves careful handling and processing to create the rice we consume. In the fields, the rice plants sway with golden grains ready for collection. Once harvested, the paddy undergoes initial processing to separate the rice grains from the husk, a delicate stage known as hulling. This is followed by milling, where the hulled rice is polished and often fortified with vitamins to enhance nutrition. Each of these steps requires precision and sophisticated machinery that ensures minimal grain loss and optimal quality. Understanding the intricacies of these processes allows us to appreciate the craftsmanship involved in delivering quality rice to our tables.
The next phases of paddy processing reveal the science of preservation and quality control. Drying is essential to reducing moisture content and preventing spoilage, while grading ensures that only the best quality rice makes it to market. The final stages involve packaging, where rice is neatly placed into bags that retain freshness. The processing plants are not merely factories; they are hubs of innovation where technology meets tradition. A small glimpse into the major operations at these facilities includes:
- Hulling: Removing the outer husk.
- Polishing: Enhancing the appearance of the grains.
- Grading: Sorting rice based on size and quality.
- Packing: Securing rice in airtight bags.
| Process Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collection of ripe rice plants. |
| Hulling | Separation of grains from husks. |
| Drying | Reducing moisture content for preservation. |
| Polishing | Enhancing grain appearance. |
Innovative Techniques in Grain Transformation: Enhancing Nutritional Value and Efficiency
In the realm of grain transformation, cutting-edge techniques are revolutionizing the way paddy is processed, ultimately leading to enhanced nutritional profiles and improved operational efficiency in processing plants. Innovations such as enzyme-assisted processing harness natural catalysts to break down complex carbohydrates and proteins, making nutrients more bioavailable. This process not only elevates the nutritional value of the end products but also reduces the reliance on harsh chemical treatments. Additionally, omics technologies, involving genomics and metabolomics, enable researchers to better understand the composition of rice varieties, fostering the development of nutrient-rich grains tailored to specific dietary needs.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technology into paddy processing plants is streamlining operations and minimizing waste. Automated systems equipped with IoT sensors monitor moisture levels, temperature, and other critical factors in real-time, optimizing the drying and storage processes. This leads to improved grain quality and reduced spoilage. The following table highlights some of the key innovative techniques being implemented:
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme-assisted processing | Utilizes enzymes to break down nutrients for better absorption. | Enhanced nutrition, less chemical use. |
| Omics technologies | Analyzes genetic and metabolic profiles for improved grain quality. | Tailored nutrients for specific health needs. |
| Smart technology | Employs IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of processing conditions. | Increased efficiency, reduced spoilage. |
Sustainable Practices in Paddy Processing: Reducing Waste and Environmental Impact
In the quest for sustainable paddy processing, innovative methods are being adopted to minimize waste and lessen the environmental impact. By focusing on waste reutilization, paddy processing plants are discovering ways to convert by-products into valuable resources. For instance, rice hulls, commonly discarded, can be repurposed into biofuel or used as a natural building material. This not only reduces the landfill burden but also contributes to a more circular economy in agricultural practices. Furthermore, water management practices—including recirculation systems and rainwater harvesting—are being integrated into processing plants to ensure minimal water wastage and maintain local water quality.
Another critical aspect of sustainable paddy processing is the implementation of energy-efficient technologies. By utilizing solar energy and biomass systems, processing plants can significantly cut carbon emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The chart below illustrates some effective technologies being utilized in the industry:
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Solar Dryers | Reduces energy costs and enhances grain quality without harmful emissions. |
| Biomass Boilers | Utilizes agricultural waste, reducing waste and providing renewable energy for processing. |
| Water Filtration Systems | Ensures clean water is reused, safeguarding local water ecosystems. |
By embracing these sustainable practices, paddy processing factories can play a pivotal role in reducing their ecological footprint while promoting a healthier environment. Ultimately, the drive for sustainability not only supports the industry but also ensures that future generations will benefit from preserved ecosystems and reduced waste streams.
Future Trends in Grain Processing Technology: Adapting to Global Demands and Market Changes
The landscape of grain processing is continuously evolving, driven by the need for efficiency, sustainability, and responsiveness to global market demands. Innovations in technology, such as automation and digital monitoring systems, are becoming increasingly prominent in paddy processing plants. These advancements not only enhance production efficiencies but also ensure consistency in product quality. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is facilitating predictive maintenance and optimized storage solutions, reducing waste and energy consumption. As farmers and processors adapt to these changes, there is also a growing emphasis on traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, as consumers increasingly demand to know the journey their food has taken.
Moreover, shifts in consumer preferences are driving the industry towards more sustainable practices. Technologies that focus on reducing water usage and energy consumption are becoming critical in the design of new processing plants. The adoption of biodegradable packaging and eco-friendly milling techniques is also gaining traction, aligning production methods with the values of environmentally conscious consumers. The emergence of plant-based food products further influences grain processing, compelling manufacturers to innovate and diversify their offerings to meet market shifts. As these trends unfold, collaboration across the supply chain will be essential for the industry to thrive in an increasingly competitive global arena.
To Wrap It Up
As we conclude our exploration of paddy processing plants, it becomes evident that these facilities are more than just machines and processes; they symbolize a vital bridge between harvest and nourishment. Each step in the conversion of raw paddy into polished rice tells a story of innovation, tradition, and sustainability. With advancements in technology and an ever-growing awareness of environmental impacts, the journey from field to fork is continuously evolving.
The transformation of grains serves not only to feed a burgeoning global population but also to reflect cultural practices and culinary traditions that span the globe. As consumers, our understanding of this intricate process enriches our appreciation for the staple that graces our tables daily.
In embracing the future of paddy processing, we also acknowledge the past, the labor, and the stewardship of the land. As we look ahead, let us continue to support sustainable practices that honor the cycles of nature while ensuring food security for generations to come. Ultimately, the rice that nourishes us is a testament to the hard work and creativity embedded in each grain—a reminder that in every bite, we partake in a global tapestry of culture and community.