Unlocking the Future of Agriculture: The Rice Milling Unit
In a world where the demand for food continues to surge alongside a burgeoning global population, agriculture stands at a pivotal crossroads. As we strive to nourish a planet teetering on the brink of sustainability, innovative solutions are paramount. Enter the rice milling unit—an unsung hero in the realm of agritech that promises to revolutionize not only the cultivation of one of the world’s staple crops but also the livelihoods of countless communities.
This article delves into the transformative potential of rice milling units, exploring how these advanced systems are redefining traditional farming practices. From enhancing efficiency and reducing waste to providing smallholder farmers with access to global markets, the rice milling unit symbolizes a harmonious blend of tradition and modernity. Join us as we unlock the future of agriculture, one grain at a time, unveiling the intricate dynamics that make rice milling a beacon of hope for sustainable farming and food security.
The Evolution of Rice Milling Technology and Its Impact on Agriculture
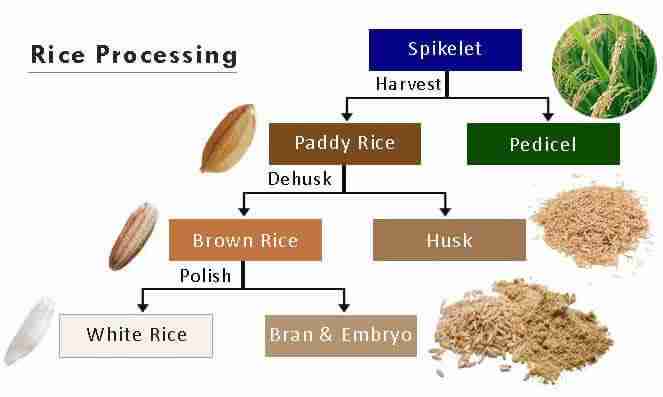
The journey of rice milling technology has been a remarkable tale of innovation and adaptation, reflecting the dynamic needs of the agricultural sector. Traditionally, milling was a labor-intensive process, often relying on manual tools such as mortars and pestles. As the agricultural landscape evolved, so did the methods for processing this staple crop. Transitioning from simple hand-operated devices to mechanized milling units, rice processing became more efficient, allowing farmers to increase yields and reduce post-harvest losses. Today, modern rice milling units employ advanced technologies that streamline the entire process, minimizing waste and enhancing the quality of the final product.
These modern solutions not only improve productivity but also have far-reaching implications for food security and rural economies. By integrating features such as automated sorting, high-efficiency milling, and environmentally friendly designs, contemporary rice milling units are adapting to the sustainable practices demanded by today’s consumers. Furthermore, the rise of small-scale milling operations has empowered local farmers, enabling them to achieve greater control over their produce while contributing to local economies. As technology continues to advance, the potential for further innovation in rice processing holds promise for redefining agricultural practices and enhancing food availability across the globe.
| Mill Type | Efficiency (%) | Energy Use (kWh/t) | Year Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Mortar | 50 | Variable | Ancient |
| Small-scale Diesel Mill | 75 | 150 | 1970s |
| Modern Automated Mill | 90 | 100 | 2000s |
Sustainable Practices in Rice Milling: Balancing Efficiency and Environment
In the current era, the rice milling industry is confronted with the dual challenge of enhancing operational efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. Implementing sustainable practices is essential for modern milling units, as they strive to reduce energy consumption and waste production. By investing in energy-efficient machinery and renewable energy sources, rice mills can significantly lower their carbon footprint. The integration of advanced technologies such as solar panels and biomass energy systems not only offsets energy costs but also promotes a cleaner production cycle. Additionally, employing water reclamation systems enables mills to recycle water used during processing, substantially reducing environmental strain during activities that traditionally generate significant waste.
To further solidify their commitment to sustainability, rice milling operations can embrace a variety of best practices that contribute to a greener future. Some of these include:
- Zero Waste Initiatives: By repurposing by-products like husk and bran for animal feed or bioenergy, mills can minimize waste and create additional revenue streams.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with local farmers and communities to implement water-saving techniques fosters social responsibility and supports regional agricultural resilience.
- Certification Programs: Achieving certifications such as ORGANIC or FAIR TRADE not only enhances marketability but also incentivizes adherence to environmentally friendly practices.
Below is a table summarizing the benefits of sustainable practices in rice milling:
| Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Upgrades | Reduced operational costs and lower emissions |
| Waste Minimization | Lower environmental impact and enhanced profit margins |
| Water Conservation | Preserved natural resources and improved sustainability |
| Community Partnerships | Strengthened local economies and enhanced food security |
Maximizing Yield: Best Strategies for Modern Rice Milling Units
To maximize yield in modern rice milling units, the integration of advanced technology and efficient processes is essential. Implementing automated sorting systems can significantly reduce manual intervention and enhance the accuracy of grain classification. Additionally, investing in high-efficiency milling machines allows for better utilization of raw materials, minimizing waste while maximizing output. Other best practices include:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensuring that machinery remains in optimal condition can prevent breakdowns and prolong service life.
- Quality Control Measures: Establish comprehensive quality checks at various stages of milling to maintain product standards.
- Training Staff: Equip employees with updated skills on milling technologies and best practices for efficient operations.
Another pivotal aspect is the adoption of data analytics to track production metrics and assess areas for improvement. Utilizing software systems that provide real-time insights can help managers make informed decisions about resource allocation and process adjustments. Coupled with sustainable practices, such as recycling waste and managing energy consumption, rice milling units can achieve substantial increases in yield. Below is a simple comparative table highlighting traditional vs. modern practices:
| Aspect | Traditional Practices | Modern Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Machinery | Manual Grinders | Automated Milling Machines |
| Quality Control | Minimal Checks | Rigorous Multi-Stage Inspections |
| Data Utilization | Basic Reporting | Real-Time Analytics & Tracking |
Empowering Farmers: The Economic Benefits of Advanced Rice Processing Techniques
Advanced rice processing techniques play a crucial role in uplifting the economic status of farmers. These innovative methods not only enhance the quality of the rice produced but also significantly reduce post-harvest losses, ultimately translating into higher profitability for farmers. By implementing modern milling systems and equipment, farmers can achieve a higher yield of milled rice, ensuring that they get the maximum return on their investment. The adoption of these techniques fosters a more sustainable approach to farming, helping farmers to garner greater market value for their products.
Moreover, collaborative initiatives between technology providers and local farmer cooperatives can lead to the establishment of centralized rice milling units. These units serve as a hub for processing, ensuring economies of scale and reducing individual operational costs. Farmers can benefit from:
- Quality Control: Advanced milling technology ensures consistent quality, enhancing market appeal.
- Cost Efficiency: Shared facilities lower expenses on maintenance and operation.
- Access to Wider Markets: Processed rice meets international standards, opening new export opportunities.
By harnessing such advanced processing techniques, farmers not only improve their livelihoods but also contribute to the overall strength of the agricultural economy.
Concluding Remarks
As we stand on the brink of a new agricultural revolution, the rice milling unit emerges not just as a tool but as a linchpin in transforming our approach to food production. By embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices, this vital unit unlocks the potential for not only increased efficiency but also higher quality yields that can contribute to global food security. As we look to the future, the rice milling unit symbolizes a commitment to adapting and evolving in the face of challenges, whether they stem from climate change, population growth, or changing dietary needs. The journey of agriculture is one of continuous learning and improvement—a journey that, with each refined grain of rice, brings us closer to nourishing the world responsibly and sustainably. The future is ripe for innovation, and with the rice milling unit leading the way, we can cultivate a landscape rich in possibility and promise.