From Grain to Gold: The Journey of Rice Milling
In the heart of countless cultures and cuisines lies a humble grain that has shaped civilizations and sustained populations for millennia: rice. This staple, revered for its versatility and nourishment, undergoes a remarkable transformation on its journey from simple paddy fields to the polished grains that grace our tables. The process of rice milling, often overlooked, is a delicate alchemy that turns raw, rough kernels into the gleaming pearls we cherish. Behind the scenes, an intricate dance of machinery and tradition unfolds—balancing the age-old techniques with modern innovations. Join us as we explore the captivating journey of rice milling, tracing each step from the vibrant farms where it begins to the bustling markets where it finds its place in our kitchens, illuminating the significance of this ancient grain in our daily lives.
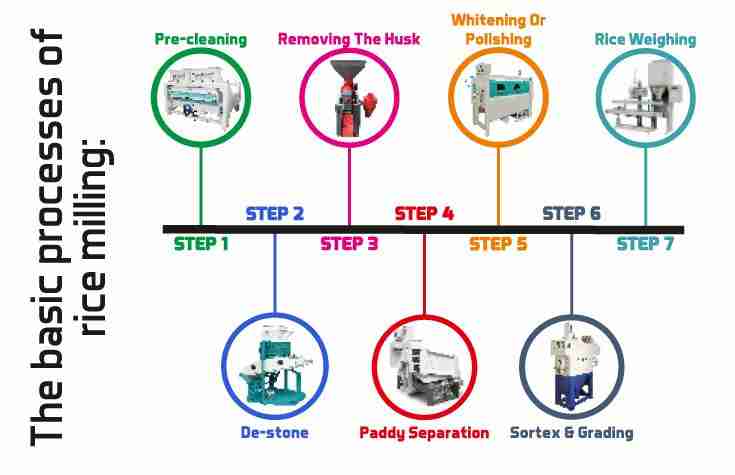
Understanding the Rice Milling Process from Harvest to Market
The journey of rice from the lush fields to our dinner tables involves a meticulous process that ensures quality and taste are preserved. Harvesting, the first crucial step, is typically performed when the grains are ripe, characterized by a golden hue and a slight firmness. Farmers utilize various methods, ranging from manual cutting to advanced machinery, to collect the rice. Once harvested, the grains undergo drying, a process essential for reducing moisture content and preventing spoilage. The dried rice is then moved to the mill, where it embarks on its transformation journey.
At the milling facility, the rice goes through several stages designed to enhance its quality. The first step is threshing, which separates the grain from the stalks. Following this, the rice is subjected to hulling, removing the inedible husk and revealing the brown rice beneath. This brown rice is then further processed through polishing, resulting in the shiny, white grains that many consumers are familiar with. The final phase involves grading and packaging, where rice is sorted based on size and quality. Meticulous care is taken at each stage to ensure that the final product meets the highest standards before reaching markets.
| Process Stage | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Harvesting | Collection of ripe rice grains | To gather products at peak maturity |
| Drying | Reducing moisture content | To prevent spoilage and enhance shelf life |
| Hulling | Removal of husk from the rice | To access edible grains |
| Polishing | Enhancing appearance of the rice | To improve marketability and consumer appeal |
Technological Innovations Enhancing Efficiency in Rice Milling
In recent years, the landscape of rice milling has been dramatically transformed by groundbreaking technologies designed to enhance productivity and streamline operations. A variety of automated and smart machinery has emerged, allowing millers to process rice more efficiently than ever before. Precision milling machines utilize advanced sensors and algorithms to optimize the milling process, adjusting parameters in real-time to reduce broken grains and improve the overall quality of the final product. Additionally, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables continuous monitoring of equipment performance, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime significantly.
Furthermore, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in rice milling plants is revolutionizing decision-making processes. These systems analyze data from previous milling operations to predict outcomes and suggest improvements, helping millers enhance their yield rates and reduce waste. Key innovations include:
- Blockchain technology: Ensures traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain.
- Solar-powered milling units: Harness renewable energy, offering sustainable solutions for rural millers.
- Data analytics: Provides insights into market trends and consumer preferences, enabling tailored production.
| Innovation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Smart Sensors | Enhance quality control by reducing broken grains. |
| Automated Systems | Decrease labor costs and increase throughput. |
| AI Algorithms | Optimize processes and predict necessary adjustments. |
Quality Control: Ensuring Premium Grains at Every Stage
In the intricate process of rice milling, every grain deserves meticulous attention, and that is where stringent measures of quality control come into play. From the moment paddy arrives at the mill, it undergoes a series of assessments to ensure its quality. This includes checking for moisture content, foreign impurities, and overall condition. Key stages of quality control involve:
- Initial Inspection: Visual and tactile examination of paddy for defects.
- Moisture Testing: Utilizing moisture meters to prevent spoilage and ensure optimal milling.
- Purity Assessment: Screening for foreign seeds and debris to guarantee a premium product.
As the grains transition through the milling stages, continuous monitoring and adjustments are essential to maintain quality standards. Achieving the perfect balance of milling—where the grain remains intact while removing the husk and bran—requires expertise and precision. Quality control personnel utilize various techniques, including:
- Color Sorting: Advanced machines remove discolored or damaged grains based on optical standards.
- Sample Testing: Regular sampling of milled rice to assess taste, appearance, and nutritional value.
- Packaging Inspections: Ensuring that packaging meets hygiene and durability standards to protect the integrity of the rice.
| Quality Parameter | Measurement Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Moisture Meters | Every Batch |
| Grain Purity | Screening Machines | Hourly |
| Color Quality | Optical Sorters | Continuous |
Sustainability Practices in Rice Milling for a Greener Future
In the quest for environmental responsibility, rice milling practices have become increasingly innovative, prioritizing sustainability at every stage of production. Tools such as water recycling systems and energy-efficient machinery not only minimize waste but also lower operational costs. Facilities are integrating technologies to reduce carbon footprints, including:
- Biomass Boilers: Utilizing rice husks as a renewable energy source.
- Solar Power: Harnessing the sun’s energy to power milling equipment.
- Water Reclamation: Systems that treat and recycle water for cleaning and processing.
Furthermore, many rice mills are adopting practices that support local ecosystems. This includes sourcing rice from farms that use organic farming methods and implementing crop rotation techniques to maintain soil health. By integrating sustainability into their supply chains, these mills are fostering a more resilient agricultural environment. Key efforts also include:
- Community Engagement: Working with local farmers to promote sustainable agricultural practices.
- Waste Reduction: Converting by-products into alternative uses, such as animal feed.
- Transparency: Providing consumers with sustainable sourcing information to make informed choices.
In Summary
As we wrap up our exploration of the intricate journey from grain to gold, it’s clear that rice milling is more than just a mechanical process; it is a symphony of tradition and technology, craftsmanship and innovation. Each stage in this journey unveils the dedication of farmers, millers, and artisans who meticulously transform humble grains into staples that sustain millions. With every bowl of rice placed on our tables, we partake in a legacy built on resilience, culture, and an enduring connection to the land.
As you reflect on the story behind your next meal, consider the unseen efforts that go into bringing rice from vast fields to your home. Let us appreciate not only the nourishment it provides but also the rich tapestry of history, effort, and passion woven into every grain. In witnessing this transformation, we gain a deeper understanding of the food we consume and the communities that thrive through its production. So, the next time you savor a dish featuring this versatile grain, remember the journey it has traveled—from grain to gold—and the lives it has touched along the way.